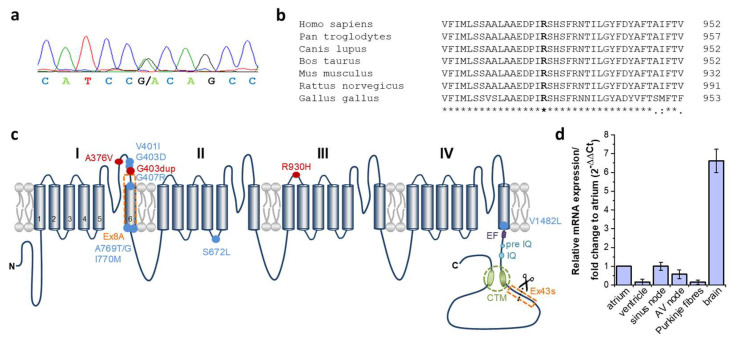
Figure 2.
Conservation and localization of the heterozygous CACNA1D variant R390H. (a) Electropherogram of the proband (III:1) with the heterozygous CACNA1D nucleotide variant c.2789G>A (NM_000720.3). The peaks represent each base in the gDNA sequence (red, thymine; green, adenine; black, guanine and blue, cytosine). (b) Multiple sequence alignment of the human CACNA1D protein region encompassing arginine 930 with orthologous protein sequences. Identical amino acids are indicated by an asterisk and highly conserved amino acids by a colon in the lower lane. The mutated amino acid residue is indicated in bold. (c) The predicted topology of the Cav1.3 channel and structure of the human transcript variants used in functional studies of Cav1.3. Cav1.3 α1-subunit comprised of four structurally homologous domains (I, II, III, IV), each containing six transmembrane spanning domains (S1–S6) together with a pore region between transmembrane helices S5 and S6. Both human Cav1.3 constructs used in expression studies (Cav1.3L and Cav1.3S) contain the alternatively spliced exon 8A in domain I (Supplementary File: Figure S1). Alternative splicing in exon 43 located in the C-terminus results in a premature stop codon lacking the distal domain of the C-terminal modulator (CTM) (referred to as Cav1.3S, Supplementary File: Figure S1) and is highly expressed in the brain, but not in the heart [20]. Mutations related to cardiac conduction disturbances are indicated by a red dot. R930H is located extracellularly in the S1–S2 linker of repeat III. Mutations related to neurologic disorders as epileptic seizures, autism or developmental delay are indicated by a blue dot and mutations related to primary hyperaldosteronism by a black dot. The EF, pre-IQ and IQ motifs function as interaction sites for calmodulin. (d) Expression of human CACNA1D exon 22 (harboring the variant at residue 930) in different human heart compartments and the brain. A real-time PCR and 2−ΔΔCt-method was used to describe the relative CACNA1D mRNA expression in different heart tissue compartments and total brain normalized to atrial CACNA1D expression.