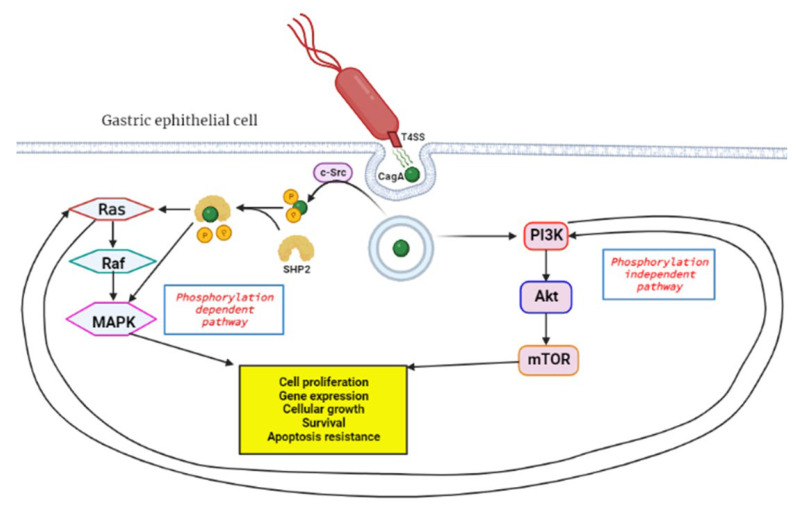
Figure 2.
Activation of RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway by H. pylori cagA oncoprotein. Upon contact with the gastric epithelial cell membrane, the bacteria’s T4SS system releases cagA through a channel, and this triggers endocytosis, a process where proteins get engulfed into the cell. In the phosphorylation dependent pathway c-Src, tyrosine kinase phosphorylates cagA, followed by SHP2 phosphatase cleavage of the phosphate groups from cagA. This leads to downstream activation of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway which favors tumorigenesis. The phosphorylation independent pathway is the PI3K/Akt/mTOR, which gets activated by cagA and results in products that induce tumorigenesis. Created with BioRender.com. (accessed on 27 September 2022).