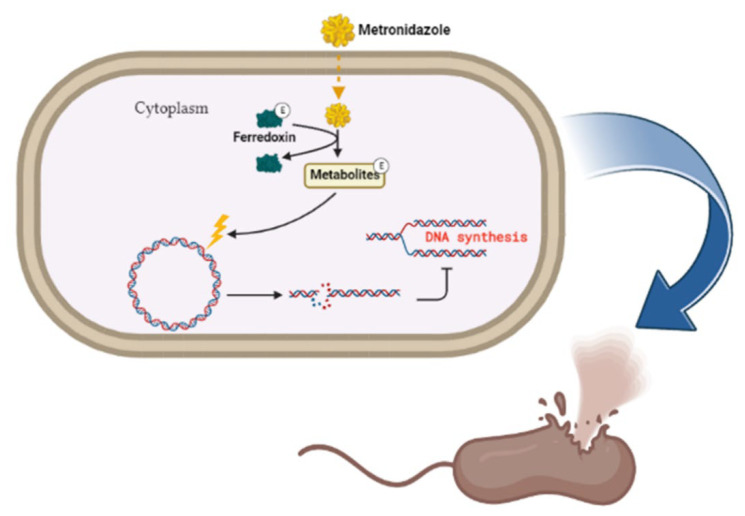
Figure 3.
Metronidazole’s mode of action. The inert drug enters susceptible bacterial cells through passive diffusion. Metronidazole is activated through its reduction by ferredoxin. Upon activation of the drug, a concentration gradient is formed, and this favors the increased uptake of the drug into the organism, thus elevating its antimicrobial effect. DNA damage subsequently leads to protein synthesis inhibition and consequent apoptosis. Created with BioRender.com. (accessed on 27 September 2022).