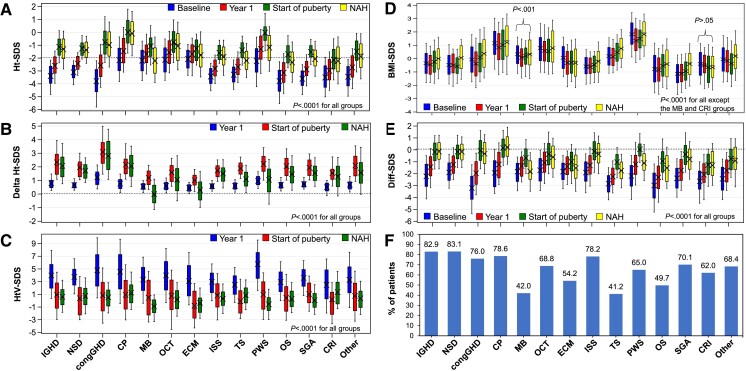
Figure 3.
Growth outcomes in the NAH subgroup (data from girls and boys combined). A, Height-SDS. B, Changes in height-SDS vs start of rhGH treatment. C, Height velocity-SDS. D, BMI-SDS. E, Difference between height-SDS and MPH-SDS. F, Percentage of patients achieving an NAH within the range of MPH ± 1.5 SDS. BMI, body mass index; congGHD, congenital GHD; CP, craniopharyngioma; CRF, chronic renal failure; Diff-SDS, height SDS minus mid-parental SDS; ECM, extracranial malignancy; GHD, growth hormone deficiency; Ht-SDS, height-SDS; HtV, height velocity; IGHD, idiopathic GHD; ISS, idiopathic short stature; MB, medulloblastoma; NAH, near-adult height; NSD, neurosecretory dysfunction; OCT, other cranial tumors; OS, other syndromes; PWS, Prader-Willi syndrome; rhGH, recombinant human growth hormone; SDS, SD score; SGA, small for gestational age; TS, Turner syndrome. SDS was calculated based on Prader references (20) for height and the reference by Cole et al (21) for BMI.