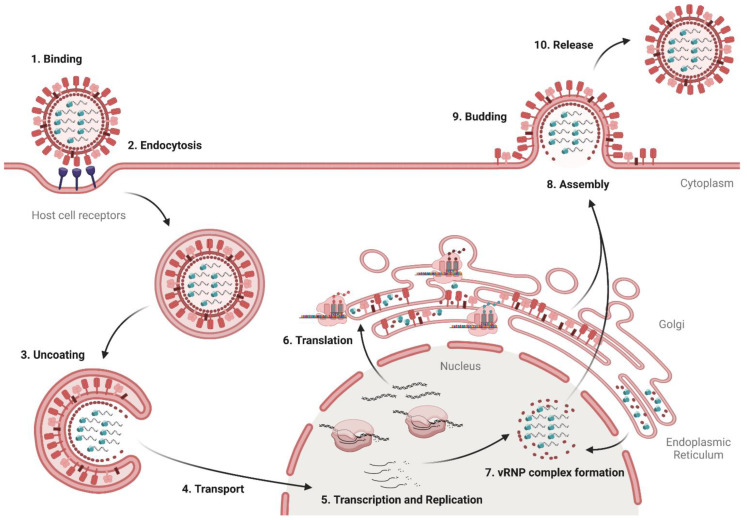
Figure 2.
Replication cycle of influenza virus. First, the virus binds via HA to sialic acid residues on the host cell (Step 1) and is taken up into the cell via endocytosis (Step 2). After acidification of the endosome and viral interior, the vRNPs are released in the cytosol (Step 3) and transported in the nucleus (Step 4), where the viral RNA is transcribed and replicated (Step 5). Viral mRNAs are transported in the cytosol for translation (Step 6). NPs and the subunits of the viral polymerase PA, PB1, and PB2 are transported back in the nucleus to form new vRNP complexes (Step 7). vRNPs and HA, NA, and M1 are transported to the cell surface for assembly (Step 8). The virion buds from the cell surface (Step 9). In the final step, NA cleaves sialic acids from the cell surface and progeny virions, enabling virus release from infected cells (Step 10). Adapted from “HIV Replication Cycle”, by BioRender.com (2022) (accessed on 20 September 2022). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates (accessed on 20 September 2022).