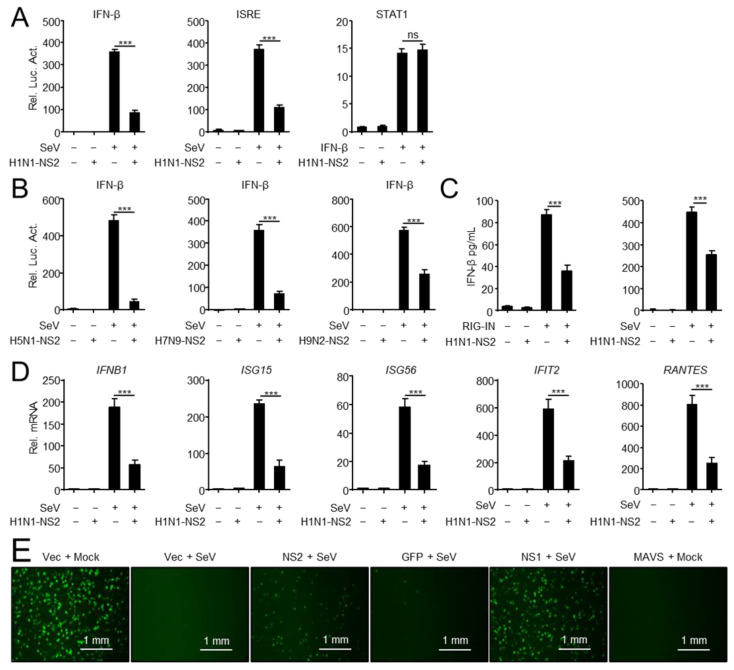
Figure 1.
NS2 inhibits IFN-I induction. (A) NS2 specifically inhibits SeV-triggered activation of IFN-β and ISRE promoter, but not IFN-β-triggered activation of the STAT1 reporter. HEK293 cells were transfected with H1N1-NS2 (200 ng) or empty vector (Vec) and the IFN-β, ISRE or STAT1 luciferase reporter, and indicated plasmids. At twenty hours after transfection, the cells were left untreated or treated with SeV for 12 h or IFN-β for 4 h before reporter assays. (B) NS2 proteins from different subtypes of IAVs inhibit SeV-triggered activation of IFN-β promoter. HEK293 cells were transfected with H5N1/H7N9/H9N2-NS2 (200 ng) or Vec and IFN-β luciferase reporter and indicated plasmids. At twenty hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before reporter assays. (C) The effects of overexpressed NS2 on RIG-IN and SeV-induced IFN-β secretion. HEK293 cells were transfected with H1N1-NS2 (200 ng) or Vec, and subsequently transfected with RIG-IN or infected with SeV. The concentration of IFN-β in supernatants was determined using human IFN-β DuoSet ELISA kit. (D) NS2 inhibits SeV-triggered transcription of IFN-β and downstream genes. A549 cells were transfected with Flag-NS2 or Vec, and subsequently left uninfected or infected with SeV (MOI = 1) for 12 h before qPCR analysis. (E) NS2 facilitates VSV-GFP replication. HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated plasmids for 24 h, and cells were then infected with SeV (MOI = 1) or not (Mock) for 24 h. Cell supernatants were inactivated by ultraviolet radiation for 20 min and collected to treat fresh HEK293 cells for another 24 h. Cells then were infected with VSV-GFP (MOI = 0.01) for 12 h, and then observed microscopically. Scale bar, 1 mm. The data shown represent three independent experiments (p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***); ‘ns’ indicates no significant difference).