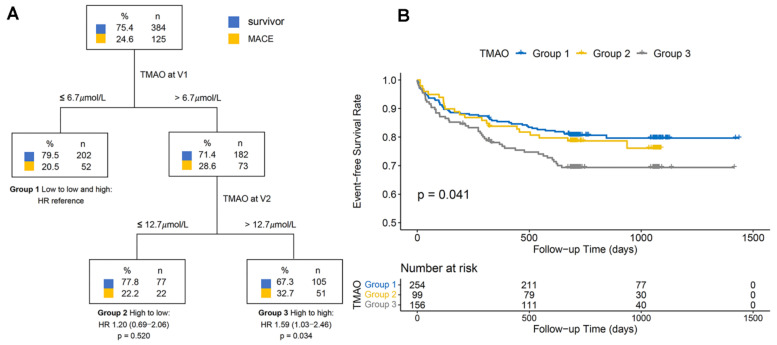
Figure 3.
Decision tree of risk stratification for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) using combined measurements at enrollment (V1) and follow-up visit (V2) for trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) (A). Kaplan–Meier curve for cumulative MACE-free survival in groups generated by decision tree (B). Decision tree using plasma TMAO level at V1 as the initial classifier, followed by plasma TMAO level at V2 enables effective selection of low- and high-risk groups of patients and increased cumulative event risk in Group 3 compared to Group 1. The number of events is shown below. Data are presented as adjusted hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The adjusted factors included age, hypertension, diabetes, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease, previous history of stroke and MI, Killip II-IV, the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events risk score, multiple vessels disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and the peak value of cardiac troponin I and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide during hospitalization, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate and left ventricular ejection fraction at V2.