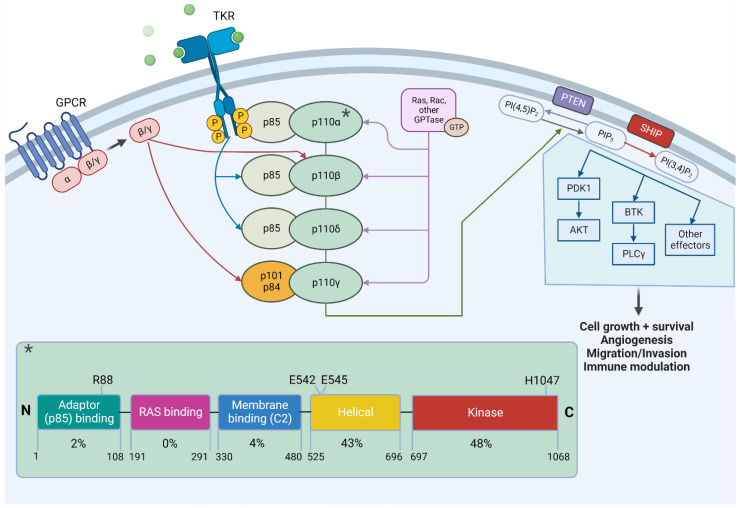
Figure 1.
PI3K pathway, structure of the p110α kinase and most frequent mutations. Class I PI3Ks heterodimers consist of a catalytic subunit (four different isoforms, p110 α/β/δ/γ) and a regulatory one (p85 and p84 isoforms). The activation of TKRs or GPCR can trigger the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. PI3K phosphorylates PIP2 to PIP3, activating the downstream effectors (including AKT) responsible for cell survival and growth. PTEN antagonizes the cascade by converting PIP3 to PIP2. In the bottom square, the five domains of p110α catalytic subunit* are detailed with their relative mutation occurrence rate (see text for details). PIP2, phosphatidyl inositol 4,5 bis-phosphate; PIP3, phosphatidyl inositol 3,4,5 bis-phosphate; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptors; TKR, tyrosine kinase receptors; Ras, rat sarcoma virus; Rac, ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; GTP, guanosine-5′-triphosphate; AKT or protein kinase B (PKB); PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; SHIP, Src homology 2 (SH2) domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 1; PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; BTK, Bruton tyrosine kinase; PLC, phospholipase C. Figure created with BioRender.com. “*” is referred to the catalytic subtunit.