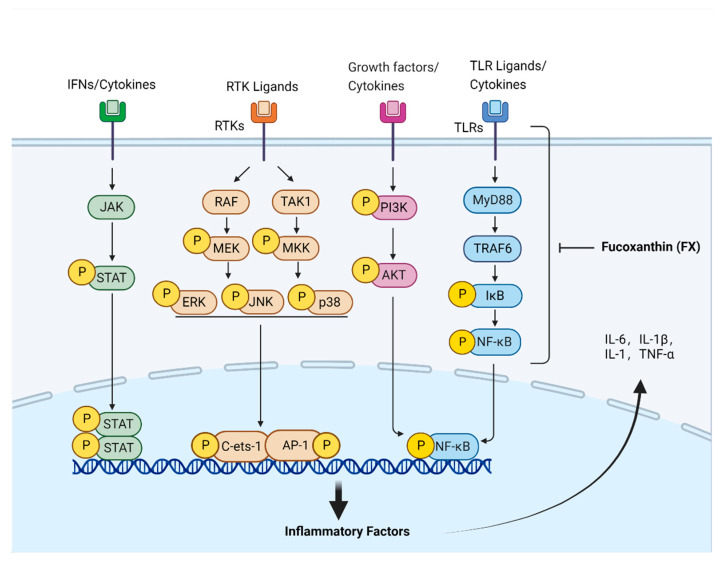
Figure 2.
Pathway underlying fucoxanthin-associated anti-inflammatory effects. The development and progression of inflammation is accompanied by the activation of JAK/STAT, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and other related signaling pathways. FX can inhibit the signal transduction of these inflammatory pathways and down-regulate the expression of inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-1β, IL-1, and TNF-α, thereby achieving the anti-inflammatory effect.