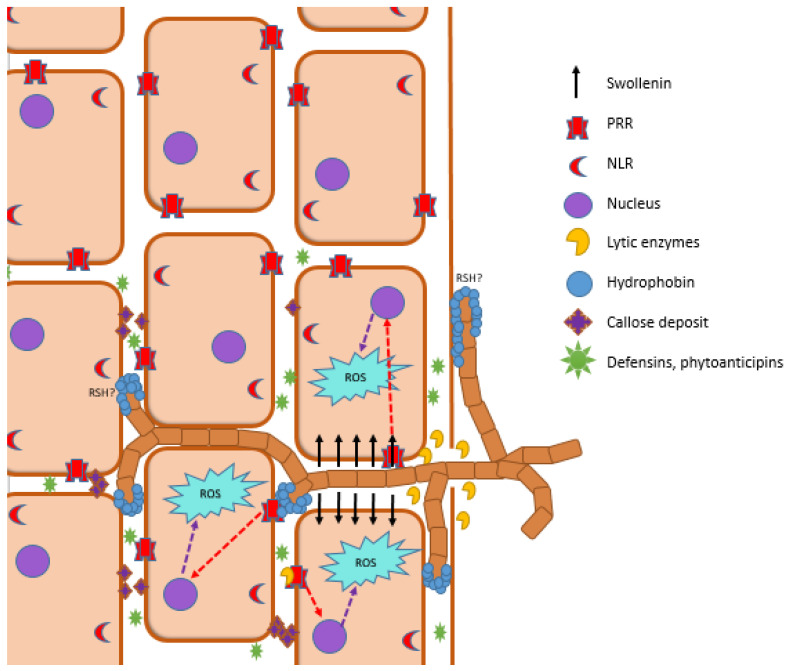
Figure 2.
Colonization of root by a fungus belonging to Trichoderma. Adhesion and protection of hyphae are mediated by the layer of hydrophobins, whereas lytic enzymes enable penetration of the epidermis. Swollenins facilitate penetration of apoplast through an expansion-like effect on plant cell walls. Recognition of Trichoderma-derived MAMP molecules (swollenins, hydrophobins, cellulolytic enzymes, and chitin) triggers plant responses to infection, i.e., synthesis of antimicrobial compounds (defensins and phytoanticipins), synthesis of the callose wall in order to physically inhibit further penetration, and overproduction of ROS and possibly also alarmones. See text for more details.