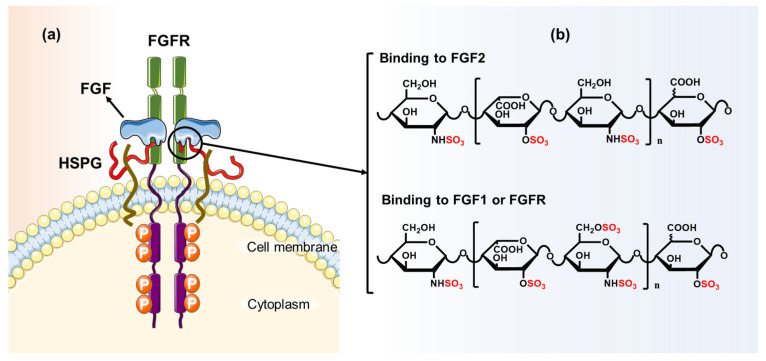
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the ternary complex of FGF/HS/FGFR and the key sites for HS binding. (a) FGFR comprises extracellular Ig-like domains, intracellular tyrosine kinase domains, and transmembrane domain. Ig-like domains bind FGF with the assistance of HS to form ternary complex; (b) HS binding to FGF2 requires 2-O-S of IdoA and N-S of GlcN; HS binding to FGF1 and FGFR requires 2-O-S of IdoA and 6-O-S, N-S of GlcN; the N-S of the nonreducing terminal residue is also necessary for HS binding to FGF/FGFR. The increased expression of HS in most tumor cells enhances FGF/FGFR signal transduction, which is beneficial to tumor cell growth and angiogenesis. (The data of the HS sequence is cited from reference [96,97,98,99]).