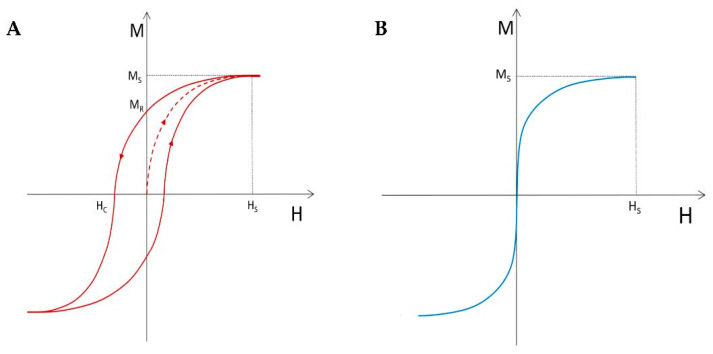
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic illustration of the typical hysteresis curve of a ferromagnetic material. Starting at field H = 0, M increases towards the saturation magnetization MS (dotted line) and then decreases following a non-reversible path. MR represents the remanent magnetization obtained when H reaches zero. HC represents the coercivity, i.e., the field to apply to nullify the magnetization. The open loop area represents the hysteresis energy losses in the material during the reversal process (heat production). (B) Typical magnetization curve of a superparamagnetic material, characterized by the absence of coercivity and hysteresis.