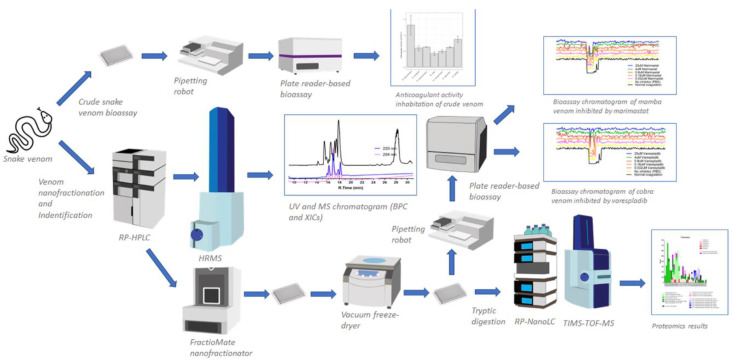
Figure 1.
A schematic overview of the complete analytical and biochemical workflow. There are two main experiments shown in Figure 1 that run simultaneously in this study: (i) crude snake venom plate reader-based bioassaying (for assessing inhibition potential of anticoagulant activity by the small molecule inhibitors varespladib and marimastat), (ii) venom separation (using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography; RP-HPLC or LC in short) coupled to UV detection followed by mass spectrometry (MS) with parallel nanofractionation for high-resolution fraction collection of separated toxins onto 384-well plates. Well plates with nanofractionated venom toxins are then vacuum centrifuged to dryness overnight, followed by bioassaying to assess anticoagulant activity. This data obtained is then processed to deliver bioassay chromatograms. Dried well plates can also be used for subsequent toxin identification by proteomics. Key: TIMS-TOF-MS, trapped ion mobility spectrometry time of flight mass spectrometry; HRMS, high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS); RP-nanoLC, reversed-phase nanoflow liquid chromatography.