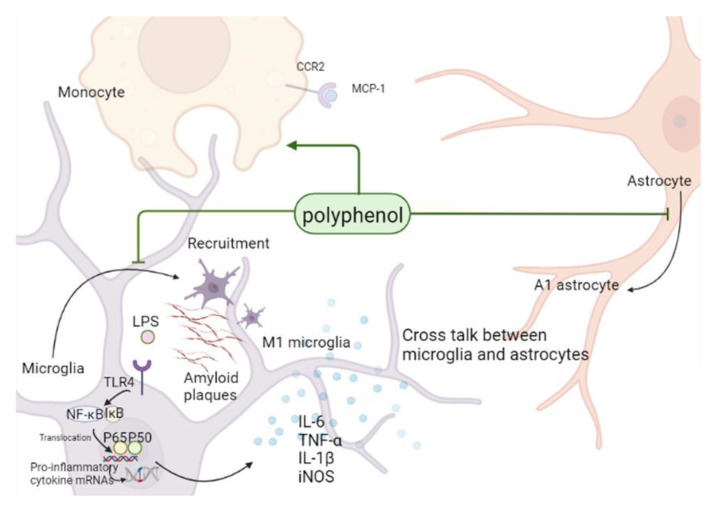
Figure 3.
Regulatory roles of polyphenols in the context of neuroinflammation: polyphenols inhibit the activation of astrocytes and transformation of microglia to pro-inflammatory phenotypes in the brain by inhibiting NF-κB pathway, reduce the secretion of inflammatory factors, improve the inflammatory environment in the brain and affect the phagocytosis of monocytes/ macrophages, to eventually alleviate AD symptoms. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-κB, tumor necrosis factor-α; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.