Figure 4.
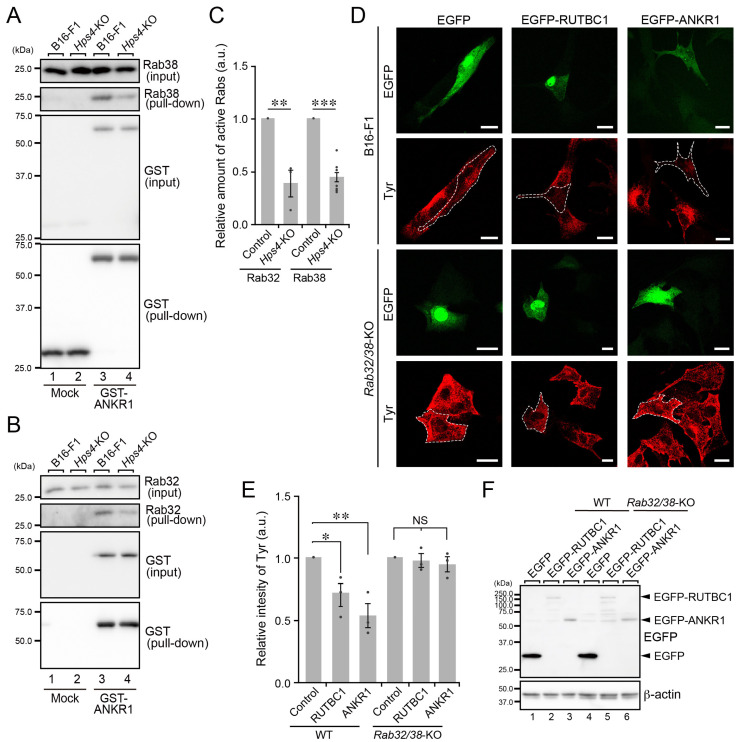
Decreased activation of Rab32/38 in Hps4-KO B16-F1 cells and Rab32/38-independent Tyr transport in Rab32/38-KO B16-F1 cells. (A) The amount of active Rab38 as determined by GTP-Rab38 pull-down assays, which were performed using the ANKR1 domain of Varp, i.e., Rab32/38 effector domain [22]. Beads coupled with GST alone (control) or GST-Varp-ANKR1 were incubated with lysates of WT cells or Hps4-KO B16-F1 cells, and the proteins bound to the beads were analyzed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated. (B) The amount of active Rab32 as determined by the GTP-Rab32 pull-down assays, which were performed using GST-Varp-ANKR1 essentially as described in (A). (C) The intensity of the active GTP-Rab32 bands (second panel in (B); n = 3) and GST-Rab38 bands (second panel in (A); n = 5) normalized by the total number of Rab32 and Rab38 bands (top panel in (A,B)), respectively, were quantified and analyzed statistically (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; Student’s unpaired t-test). (D) Representative Tyr images (red) of WT cells and Rab32/38-KO B16-F1 cells expressing either EGFP alone, EGFP-RUTBC1 [29], or EGFP-ANKR1 [31]. The EGFP-expressing cells (green) are outlined with broken white lines. Scale bars, 20 μm. (E) Relative intensity of Tyr in the WT cells and Rab32/38-KO B16-F1 cells shown in (D). The graph shows the means and SEM of the data obtained in three independent experiments (n > 10 cells in each experiment). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant (Dunnett’s test). (F) Expression of EGFP-tagged proteins in WT cells and Rab32/38-KO B16-F1 cells. Lysates of the cells indicated were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP (top) and β-actin (bottom).