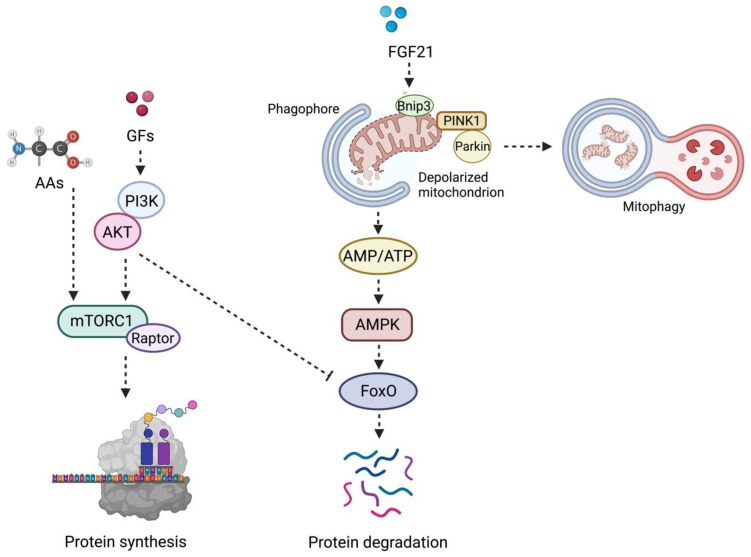
Figure 1.
Schematic Representation of the Coordinated Regulation of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin and Mitophagy in Muscle Protein Synthesis and Degradation. In the presence of growth factors (e.g., insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1, growth hormone), the phosphoinositide 3-kinases-protein kinase B (PI3K) is activated and triggers muscle protein synthesis via the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). The latter complex is also positively modulated by amino acid availability. Conversely, downregulation of PI3K signaling induces translocation of Forkhead box O (FoxO) into the nucleus, where it regulates the transcription of the ubiquitin-ligases muscle ring finger 1 (MuRF1) and muscle atrophy F-box (MAFbx) genes. The activation of this signaling pathway induces degradation of sarcomere components and ignites a muscle pro-atrophy response. The same degradative molecular program is also triggered by fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in the setting of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. In this case, the release of FGF21 stimulates the expression of the mitophagy-related protein B-cell lymphoma 2 interacting protein 3, paralleled by recruitment of the phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) through the translocases of the inner and the outer membranes and its activation at the site of depolarized mitochondria. This event promotes the sequestration of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin at the outer mitochondrial membrane and guides the clearance of dysfunctional organelles. Finally, depolarized mitochondria are coated and prepared for disposal by the ubiquitin-binding adaptor protein p62/sequestosome-1 and the recruitment of the microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (LC3). This enables the transfer of mitochondria to lysosomes. FoxO-dependent atrophy is also pursued when severely damaged and bioenergetically incompetent mitochondria are not efficiently removed and, thus, the AMP/ATP ratio increases, which engages 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Abbreviations: AA, amino acid; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; GF, growth factor; TIM23, translocase of the inner membrane 23; TOM, translocase of the outer membrane. Created with BioRender.com, accessed on 26 August 2022.