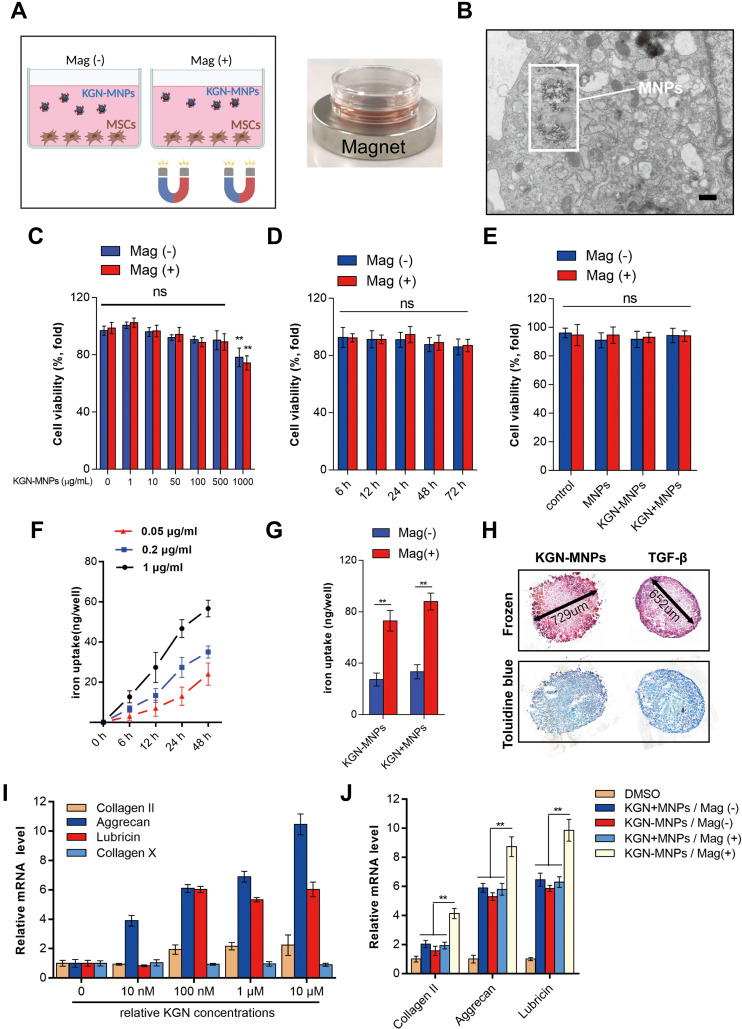
Figure 2.
Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity test of KGN-MNPS. (A) Schematic illustration and images of the cell culture protocol. (B) TEM image of KGN-MNP internalization and encapsulation in MSCs (scale bar= 6 μm). (C) MSC viability after 24 h of incubation with different concentrations of KGN-MNPs. (D) No significant changes in cell viability were detected with incubation of KGN-MNPs at different time points with or without a magnet. (E) MSC viability after 24 h of incubation with different suspensions showed that none of the tested products were toxic to the cells. (F) The cellular uptake of KGN-MNPs was time and concentration dependent. (G) Magnet significantly enhanced the cellular uptake of nanoparticles, **p<0.01. (H) KGN-MNPs induce MSCs into chondrocytes in vitro. (I) KGN-MNPs increased chondrocyte-specific gene expression but not Collagen X expression in MSCs. (J) Chondrocyte-specific gene expression in MSCs after KGN-MNPs incubation for 72 h with or without the presence of a magnet, **p<0.01.
Abbreviations: ns, not significant; KGN, kartogenin; MNPs, magnetic nanoparticles; Mag (+), in the presence of magnet; Mag (-), in the absence of magnet; KGN+MNPs, mixture of KGN and MNPs without reaction; KGN-MNPs, KGN-loaded MNPs.