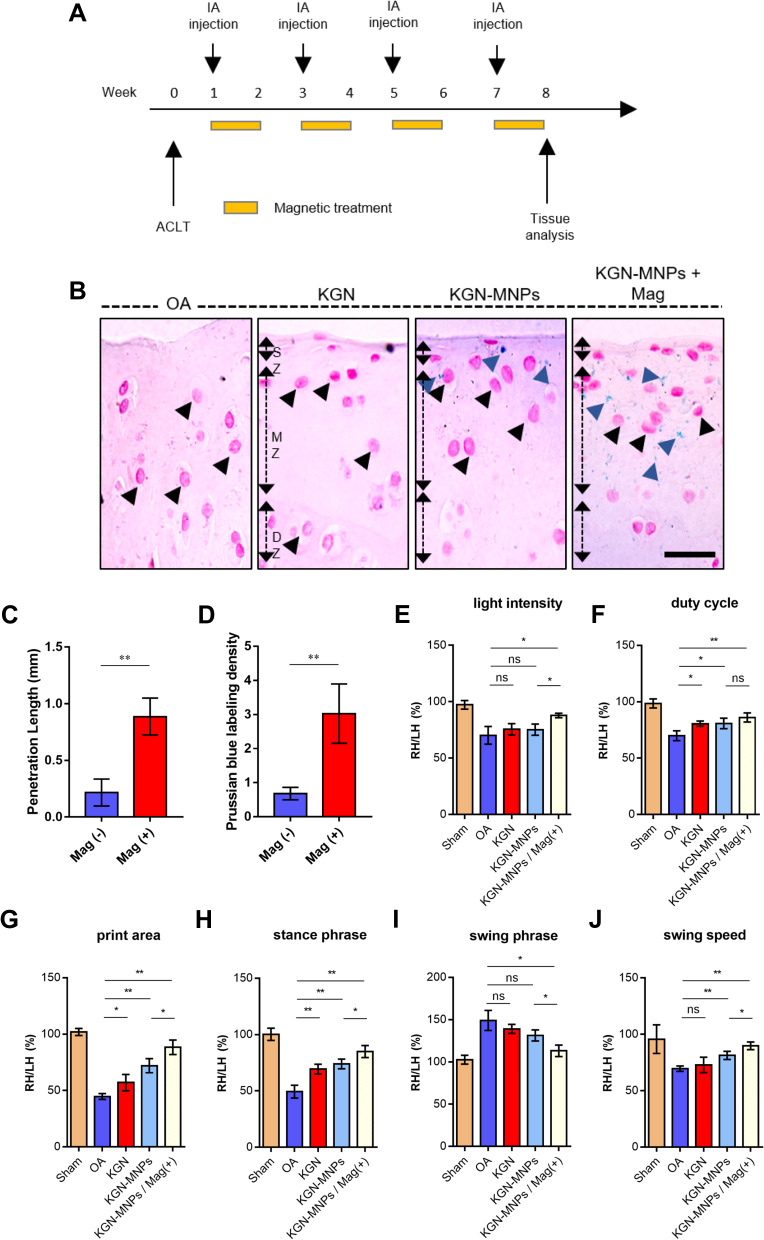
Figure 3.
KGN-MNPs exhibit enhanced penetration and show efficacy in improving rat movement disability caused by OA. (A) Diagram of in vivo performance. (B) KGN-MNPs not exposed to magnets primarily remained in the SZ of cartilage, whereas the application of additional magnetic force increased the penetration into the MZ. Note the enhanced retention ability of the magnet; large amounts of MNPs could be observed in the matrix of the SZ and MZ (scale bar= 200 μm). (C) The magnet could significantly increase the penetration length of KGN-MNPs into the cartilage. (D) The magnet significantly increased the amount of KGN-MNPs in the cartilage. (E–J) The gaits of rats were analyzed using the Catwalk gait analysis system. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Abbreviations: ns, not significant; KGN, kartogenin; MNPs, magnetic nanoparticles; Mag, magnet; KGN-MNPs, KGN-loaded MNPs.