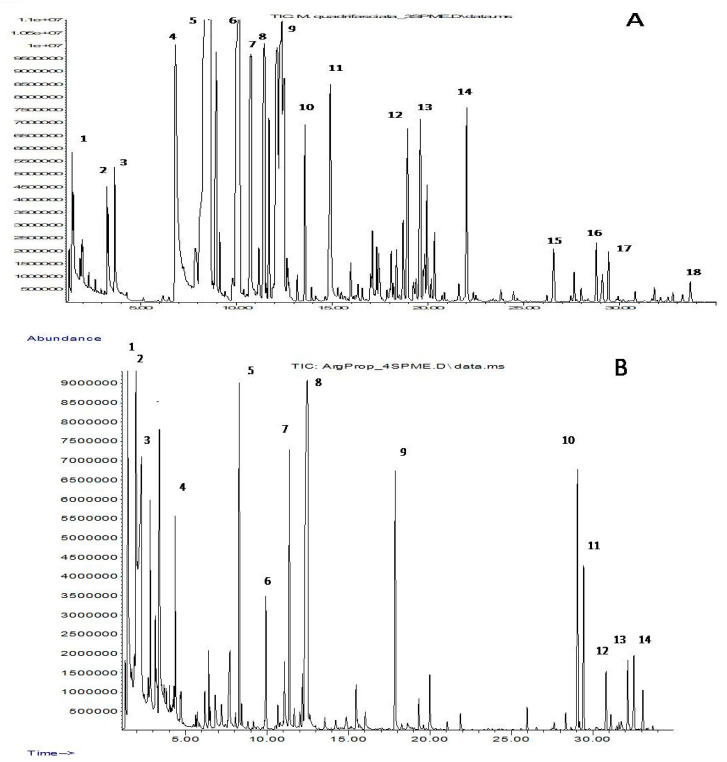
Figure 1.
Chromatogram of the volatile components in propolis M. quadrifasciata (A) and T. fiebrigi (B). (A) 1—ethanol, 2—pyridine, 3—toluene, 4—styrene, 5—α-pinene, 6—β-pinene, 7—myrcene, 8—3-carene, 9—limonene, 10—γ-terpinene, 11—terpinolene, 12—4-terpineol, 13—α-terpineol, 14—methyl carvocrol, 15—α-copaene, 16—longifolene, 17—β-caryophyllene and 18—δ-cadinene. (B) 1—ethanol, 2—ethyl acetate, 3—acetic acid, 4—ethyl butanoate, 5—α-pinene, 6—β-pinene, 7—3-carene, 8—2-ethylhexan-1-ol, 9—2-ethylhexyl acetate, 10—α-gurjunene, 11—β-caryophyllene, 12—α-humulene, 13—β-selinene and 14—α-selinene.