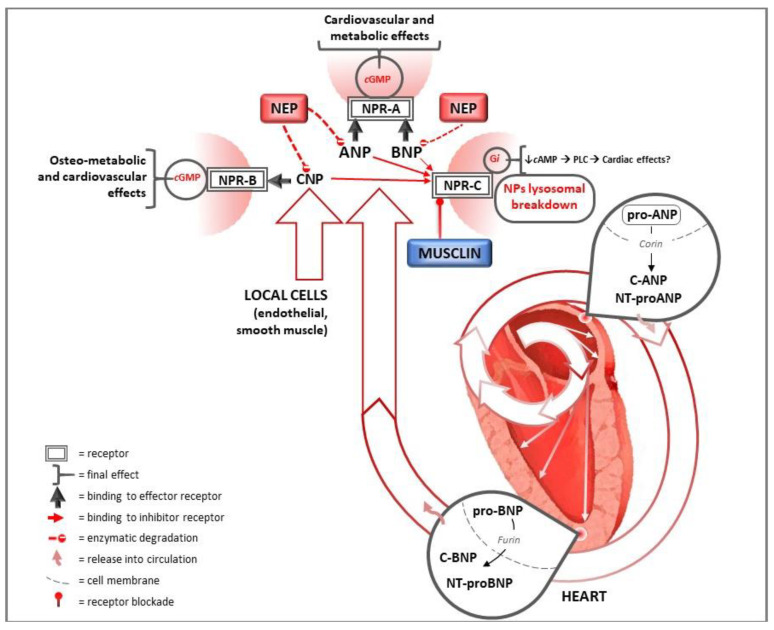
Figure 2.
Natriuretic peptides pathways for heart and cardiovascular protection. ANP and BNP are synthesized in response to wall hemodynamic stress as precursor proteins in the heart and subsequently released into circulation after cleavage in their active form. CNP is mainly produced by endothelial cells. They exert several cardiac and systemic effects on the target organs, including the heart, binding to NPR-A and NPR-B. Their degradation is mediated by binding to NPR-C and by neprilysin. In this context, musclin competitively binds NPR-C, inhibiting NPR-C-mediated NPs degradation. Nep: neprilysin; ANP: atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide; CNP: C-type natriuretic peptide; NT: N terminal; NPR-A: natriuretic peptide receptor A; NPR-B: natriuretic peptide receptor B; NPR-C: natriuretic peptide receptor C; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Gi: inhibitory G protein; PLC: phospholipase C.