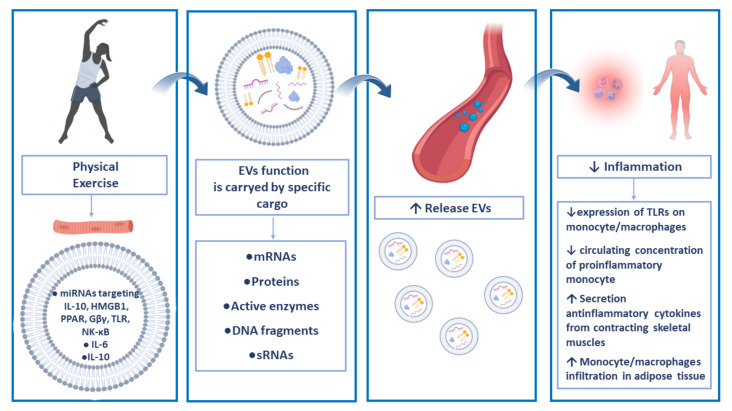
Figure 1.
Physical exercise and anti-inflammatory effects of EVs. Physical exercise induces the release of EVs of different origins. It has been demonstrated that exercise training induces the secretion of EVs stemming from skeletal muscle cells that carry anti-inflammatory signaling molecules (miRNAs and cytokines). Once released, (leukocyte-, muscle-, and platelet-derived EVs) EVs act locally and systemically reaching target tissues throughout blood circulation. EVs produced by physical exercise therefore act as anti-inflammatory agents.