FIG. 1.
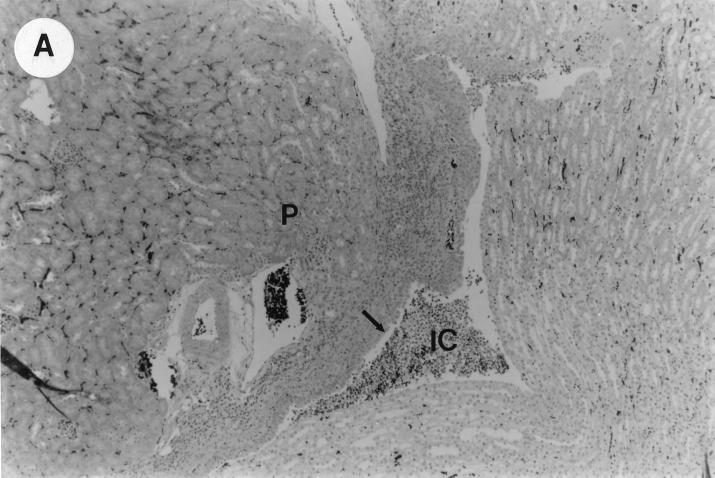
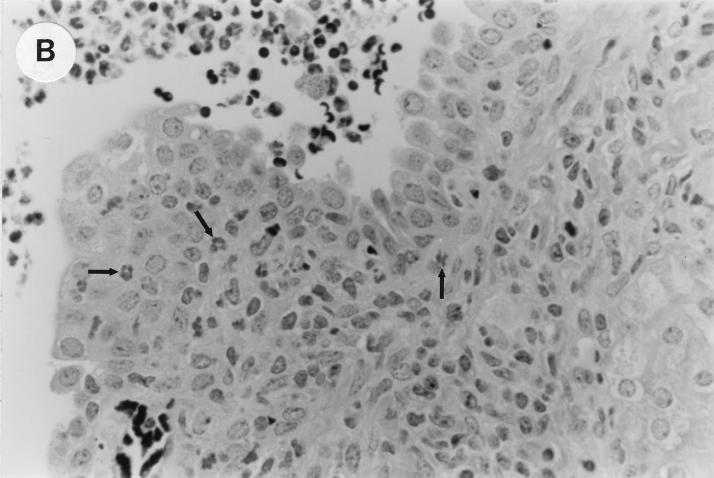
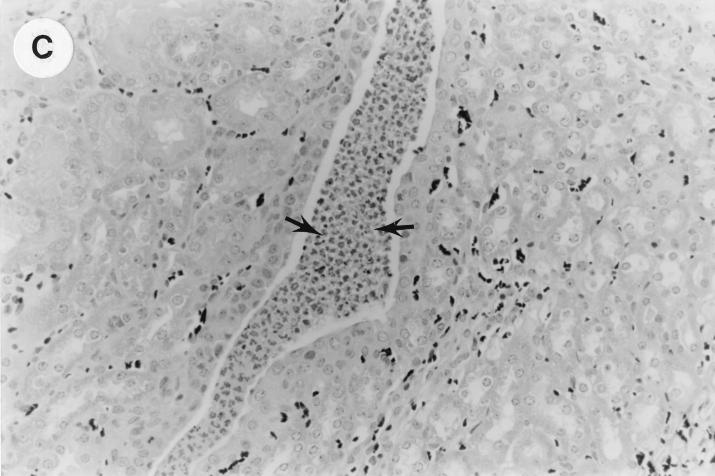
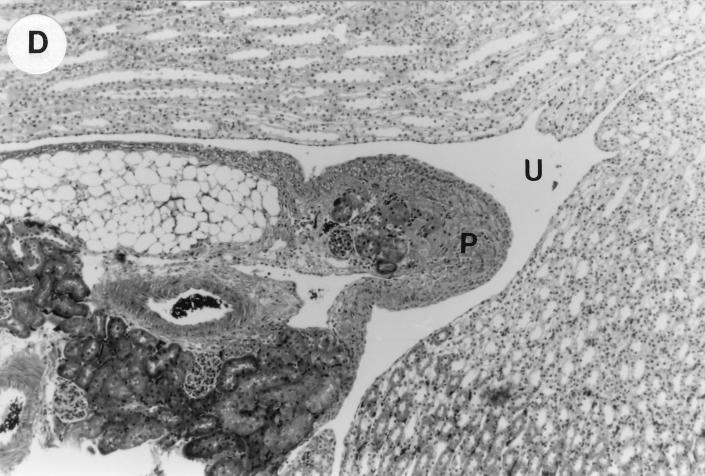
UTI by E. coli Dr+ in C3H/HeJ mice leads to acute and chronic inflammation of kidneys. (A) Representative renal pathology in kidney sections obtained from mice infected with E. coli Dr+ at 35% gestation and sacrificed after preterm delivery revealed 1 to 2+ acute (PMN infiltration) and chronic (MNC infiltration) in the pelvis by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The arrow points to renal pelvis with inflammatory cells. Abbreviations: IC, inflammatory cells; P, renal pelvis. Magnification, ×64. (B) Higher-power view of Fig. 1A focussed on renal pelvic urothelium showing neutrophils (indicated by the arrows). Magnification, ×400. (C) Higher-power view of Fig. 1A showing renal tubular involvement. The arrows point to renal tubule with large number of PMNs within one tubular lumen. Magnification, ×200. (D) Normal histopathological appearance of a kidney section from the E. coli Dr− group or control group with absence of MNC infiltration. Abbreviations: U, urinary space; P, renal pelvis. Magnification, ×80.