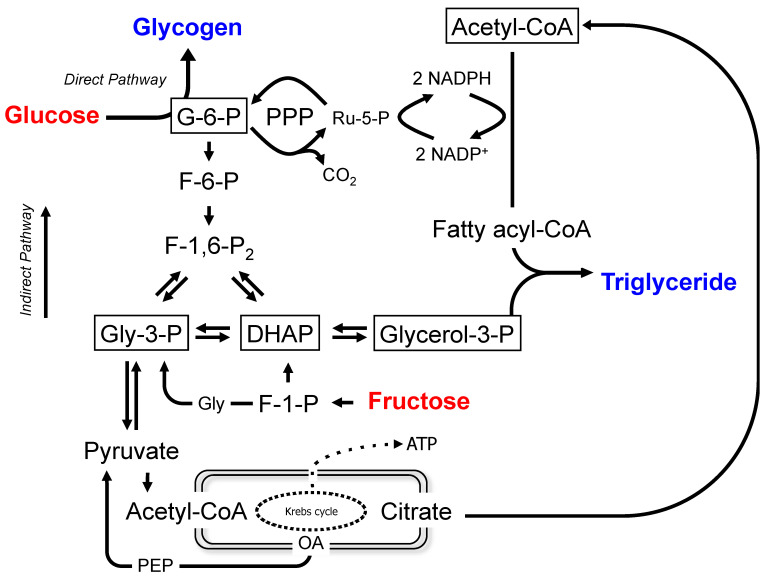
Figure 1.
Metabolic model for the synthesis of glycogen and triglyceride from glucose or fructose in the liver. The model includes glucose-6-phosphate oxidation by the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) to provide NADPH for conversion of acetyl-CoA to fatty acyl-CoA via de novo lipogenesis. The 13C-enriched glucose and fructose precursors are highlighted in red and the sampled metabolites, glycogen and triglyceride, are highlighted in blue. The metabolite pools whose 13C and 2H enrichments are reported by the sampled metabolites, namely, glucose-6-P, triose-P (dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) and lipogenic acetyl-CoA, are highlighted in boxes. Glycogen synthesis from glucose via glucose-6-P from gluconeogenic precursors, including pyruvate and triose-P sources, is also indicated (direct and indirect pathways, respectively). For simplicity, some metabolic intermediates, as well as ATP/ADP and NAD/NADH interconversions, are not shown. Abbreviations are as follows: DHAP—dihydroxyacetone phosphate; F-1-P—fructose-1-phosphate; F-6-P—fructose 6-phosphate; F-1,6-P2—fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; G-6-P—glucose 6-phosphate; Gly—glyceraldehyde; Gly-3-P—glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; OA—oxaloacetate; PEP—phophoenolpyruvate; Ru-5-P: ribulose-5-P.