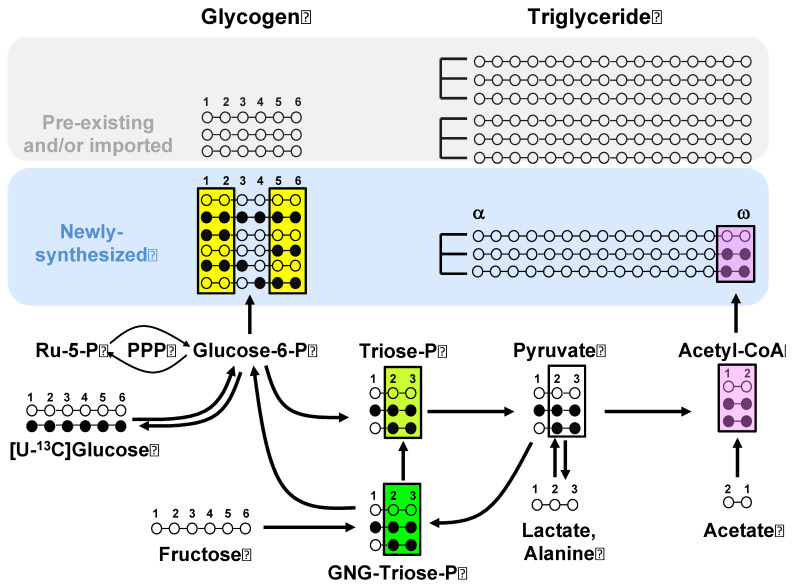
Figure 2.
13C-Isotopomers of selected metabolic intermediates generated from [U-13C]glucose metabolism into lipogenic and glycogenic pathways. These include hepatic glucose-6-P—inferred from the analysis of newly synthesized glycogen; triose-P recruited for gluconeogenesis (GNG-triose-P)—inferred from the analysis of indirect pathway glycogen 13C-isotopomers; triose-P supplying glycerol-3-P for fatty acid esterification and acetyl-CoA units for de novo lipogenesis—inferred from the 13C-isotopomer analysis of newly synthesized triglyceride glycerol; and the acetyl-CoA pool supplying lipogenesis—inferred from the 13C-isotopomer analysis of newly synthesized fatty acids. For the metabolite carbon skeletons, the filled and unfilled circles represent 13C and 12C, respectively. The shading highlights those 13C-isotopomers that inform the enrichment of the lipogenic acetyl-CoA pool by [U-13C]acetyl CoA from both glycolytic precursor and fatty acid product perspectives, and the colors indicate isotopic enrichment equivalence (same color) or non-equivalence (different colors). For simplicity, in depicting the fatty acid labeling, only the 13C-isotopomers of the last two fatty acid carbons (representing the first acetyl-CoA moiety to be incorporated into de novo lipogenesis) are shown.