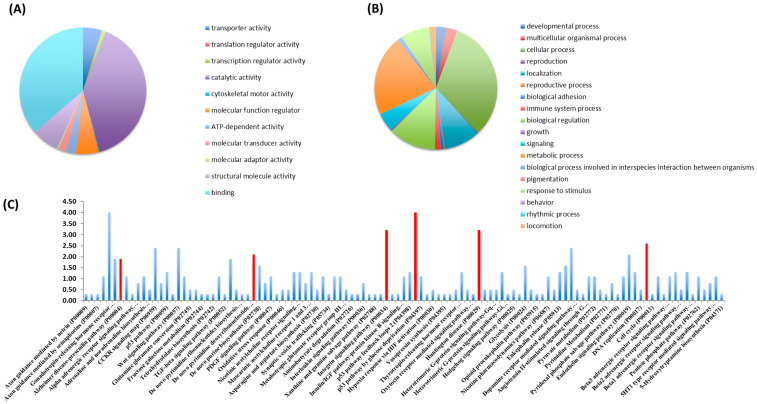
Figure 1.
Classification of proteins identified in Nosustrophine based on their molecular functions and biological processes. Nosustrophine extracts (1 mg) were mixed with tagged peptides before being fractionated and separated using nano-flow LC-coupled to a high-resolution trapped ion mobility spectrometry (TIMS) on a quadrupole TOF (Q-TOF). This was followed by bioinformatic analysis with the PANTHER Classification System. Pie charts depicting (A) molecular functions, and (B) biological processes, of 517 identified proteins, based on UniProt/Swiss-Prot databases are shown. (C) The proteins found in Nosustrophine control numerous pathways, some of which are associated with neurodegenerative illnesses such as Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease (presenilins), and Parkinson’s disease. The extract contains many proteins involved in chemokine and cytokine-mediated inflammation, integrin and Wnt signaling, and cytoskeletal control by Rho GTPase (red bars).