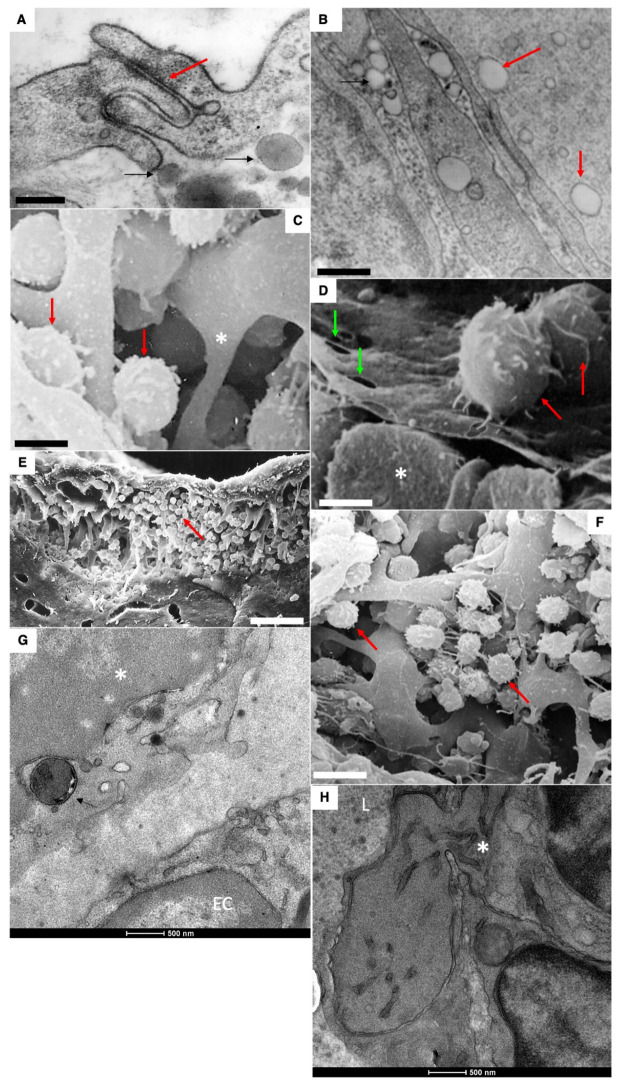
Figure 8.
Mechanisms of resorption of large ChMs from the interstitial space into LCs of a newborn rat after feeding. (A,B) The lumen of LC is filled with ChMs (shown by the arrow). Large lipid droplets are visible in the interstitial (shown by the black arrows). (B) Interdigital contact between endothelial cells in LCs does not allow ChMs (arrows) to pass through it. (C–H) Migration of macrophages into subcapsular sinus of lymph node after the first feeding. Uptake of large chylomicrons by macrophages (G). Red arrows in all images indicate leucocytes. White asterisks demonstrate monocytes. Green arrows show pores in endothelial cells surrounding the sinus from the follicular side. Scale bars: 420 nm (A); 560 nm (B); 5.4 µm (C); 4 µm (D); 30 µm (E); 10.8 µm (F). In images (G,H), scale bars are below images and are equal to 500 nm.