Figure 9.
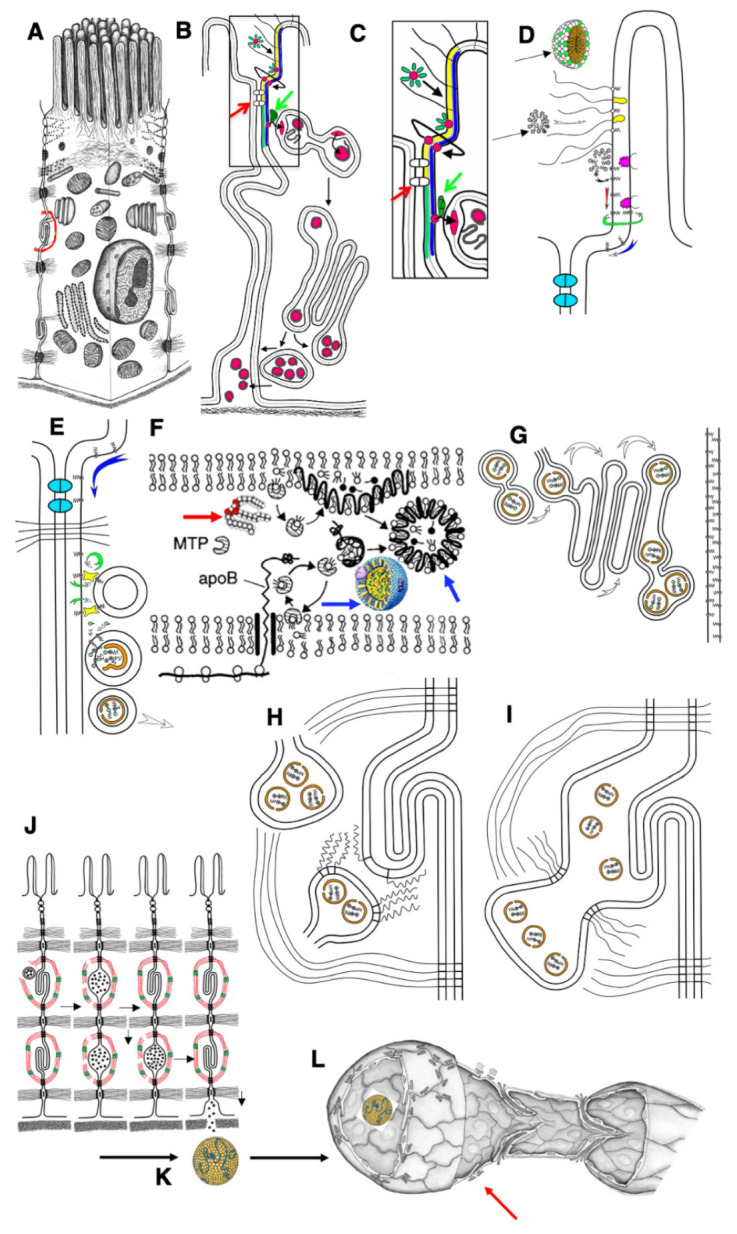
Schemes of the mechanisms of lipid transcytosis across enterocytes and their uptake by lymphatic capillary in adult rats (adapted from [4]). (A) Enterocyte. (B) The gut micelle (red ring surrounded with green ovals) is composed of free fatty acids (FFAs), cholesterol and bile acids (green ovals). The micelle passes through glycocalyx (black lines) and contacts with the external leaflet of the apical plasma membrane (APM; yellow layer). Then, FFAs and cholesterol are subjected to flip-flop (the bent line shows this path of red ring) and appear in the cytosolic leaflet of the APM (blue layer). (C,D) Higher magnification of the pathways shown in (B). (D) The micelles (black arrows) pass through glycocalyx (white arrow). Membrane proteins containing long polysaccharide chains of glycocalyx are yellow. Caveolin is magenta. FFAs (dots, black center) are inserted into the lipid bilayer of the APM, and then diffuse along the external leaflet (red arrow) or flip-flop (green arrow) and then diffuse along the cytosolic leaflet (blue arrow). This pathway allows FFAs to reach the basolateral plasma membrane because the FFA diffusion along the external leaflet is restricted by proteins of tight junctions (indicated with red arrows in (B) and (C) or colored in light blue in (D). (C) FFAs bypass tight junctions (white dots situated between APM are indicated with red arrow) and reach the sites where cisternae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum are attached to the basolateral PM along with lipid transfer proteins (green dot indicated with green arrows). (E) These proteins (green arrows in (B) and (C)) constantly (circular green arrow) transfer FFAs and cholesterol through cytosol into the cytosolic leaflet of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum membrane (the arc-like green arrow). (F) Then, FFAs are transformed into triacylglycerols and cholesterol ethers (double-headed structures, one green dot in (E)). Finally, these are extracted from smooth endoplasmic reticulum membranes and ApoB (orange) forms pre-chylomicrons. (D) Diffusion of FFAs along PM. (E) Delivery of lipids into membrane of smooth ER attached to the BLPM of enterocyte. (F) ApoB protein (black line) is synthesized by ribosome (white double rings below lipid bilayer of the ER). Then triacylglycerols (thick red arrow) and cholesterol ethers are captured by ApoB and MTP protein and the chylomicrons (blue arrows) are formed. (G) Pre-chylomicrons are transported from the ER at the Golgi complex, where mature chylomicrons are formed and concentrated in distensions and at the trans side (white arrows). (H) Post-Golgi carriers are formed, connected with the Golgi complex, and then fuse with the basolateral plasma membrane of the interdigitating contacts with the help of SNAREs (zip-like lines). (I) Chylomicrons are in the extracellular space within interdigitating contacts. (J) Contraction of actin–myosin cuff (red–green) induces movement of chylomicrons towards basolateral membrane and their passage through the BM pores. (K) Chylomicrons (yellow) are delivered to the interstitial space. (L) Chylomicrons are captured by lymphatic capillary (red arrow) and delivered into its lumen through the inter-endothelial contacts of endothelial cells.
