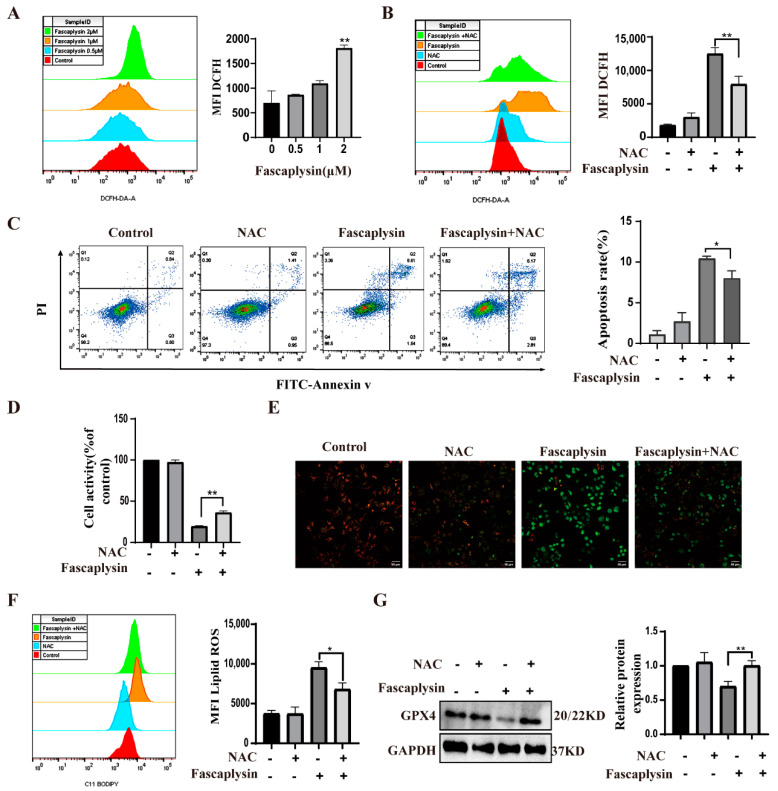
Figure 5.
ROS played an important role in fascaplysin-induced apoptosis in A549 cells. (A) ROS in A549 cells was detected by flow cytometry with DCFH−DA probe. (B) ROS was detected by flow cytometry after treatment of A549 cells with the NAC (1 mM) and fascaplysin (2 μM), alone or in combination, for 3 h. (C) A549 cells were treated with NAC and fascaplysin, alone or in combination, and then apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry after double staining with annexin V-FITC/PI. (D) Cell viability was measured by CCK-8. (E) MMP changes were analyzed with a JC-1 probe. (F) A549 cells were treated with fascaplysin and NAC, alone or in combination, and lipid ROS levels were measured with a C11 BODIPY probe. (G) A549 cells were treated with fascaplysin and NAC, alone or in combination, and GPX4 protein expression levels were detected by Western blotting. Analysis results represent mean ± SD, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.