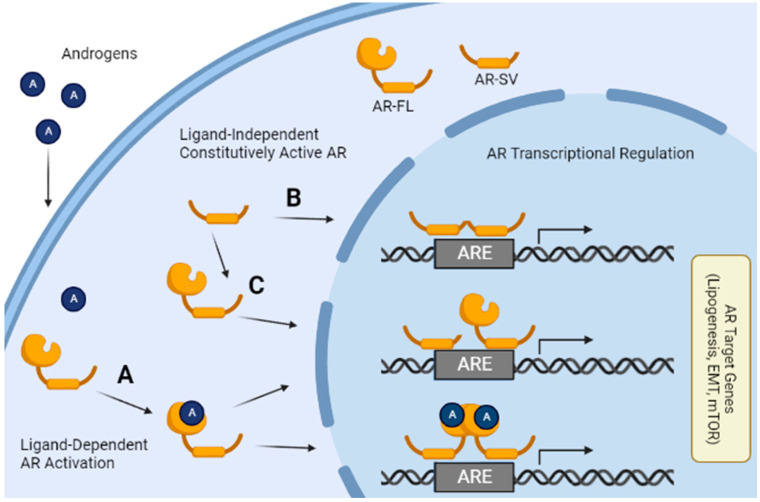
Figure 4.
Illustration of mechanisms of ligand-independent and ligand-dependent AR-mediated transcriptional regulation. (A) Androgens bind to the LBD of AR-FL leading to nuclear localization, dimerization, and binding of the DBD to androgen response elements (AREs) in the DNA. (B) In the absence of androgens AR-SVs both dimerize and localize to the nucleus. (C) In the absence of androgens, AR-SVs are also able to facilitate AR-FL nuclear localization without androgen binding to the LBD. These various methods of AR activation ultimately result in the regulation of AR target genes and more broadly gene pathways such as lipogenesis, EMT, and mTOR-related pathways. Figure created in BioRender.