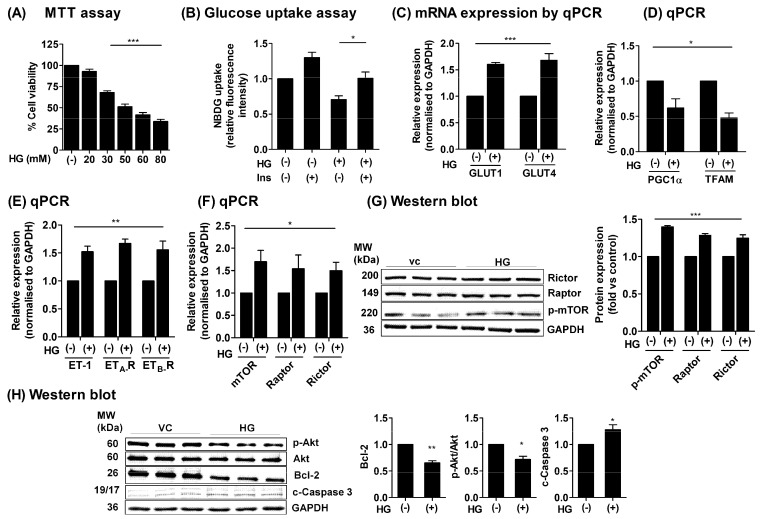
Figure 1.
Effect of high glucose (HG) treatment in H9c2 cells. (A) The H9c2 cells were seeded in low glucose DMEM medium (5.5 mM) and treated with various concentrations of D-glucose-containing medium (vc = vehicle control, 20 mM, 30 mM, 50 mM, 60 mM, and 80 mM) for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. (B) The H9c2 cells were seeded in low glucose DMEM medium overnight and incubated with HG medium for 24 h and subjected to 2-NBDG-based glucose uptake assay. The fluorescent intensity was measured at wavelengths λex/λem: 485/530 nm. (C–F) The H9c2 cells were treated with HG for 24 h, and total RNA was extracted. The mRNA expression level of GLUT1, GLUT4, ET-1, ETA-R, ETB-R, mTOR, Raptor, Rictor, PGC1α, and TFAM genes were determined by qPCR and normalized to GAPDH and expressed as fold versus non-treated controls (vc) (2−ΔΔCT). (G,H) The H9c2 cells were treated with HG as above, and proteins were extracted after 24 h of incubation. Protein expressions of p-mTOR/Raptor/Rictor (G) and survival markers p-Akt, Akt, Bcl-2, and c-Caspase-3 (H) were determined using western blotting. N = 3; Mean ± S.E.M.; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.