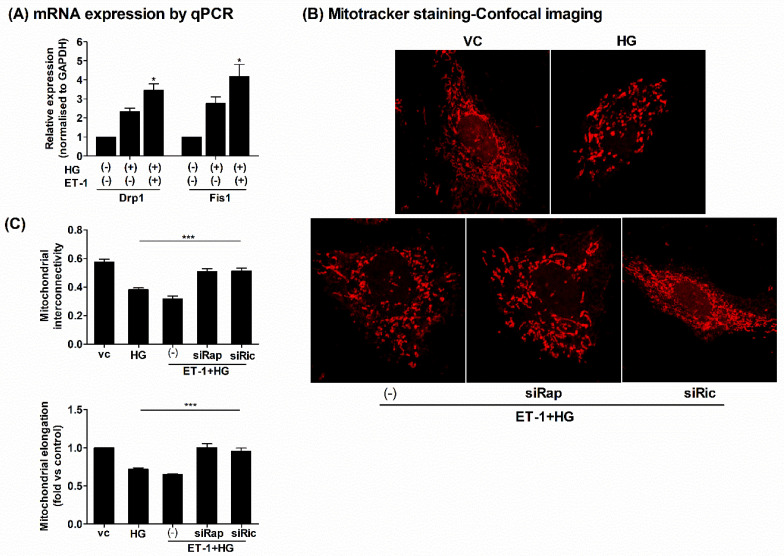
Figure 4.
Inhibition of mTOR improved the mitochondrial damage under HG conditions in H9c2 cells. The H9c2 cells were seeded in 12-well culture dishes on gelatin-coated coverslips in low glucose DMEM medium. Next, the cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting Raptor/Rictor or control siRNAs for 24 h followed by ET-1 (20 nM) treatment for 3 h, followed by HG treatment for another 24 h. (A) The total RNAs were extracted, and q-PCR was performed to assess mRNA expressions of mitochondrial fission-related genes Drp1 and Fis1. The mRNA expressions were normalized to GAPDH and expressed as fold versus controls (vc) (2−ΔΔCT). (B) At the end of designated treatments, mitochondrial morphology was assessed, employing MitoTracker red labeling using confocal microscopy, and quantification is depicted in figure (C); the mitochondrial interconnectivity indicative of fragmentation/fission was calculated as area/perimeter ratio while mitochondrial elongation indicative of size was calculated as inverse of circularity and expressed as fold relative to control. At least 25–30 cells per group from three independent experiments were analyzed using Image J software (NIH). N = 3; Mean ± S.E.M.; * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001.