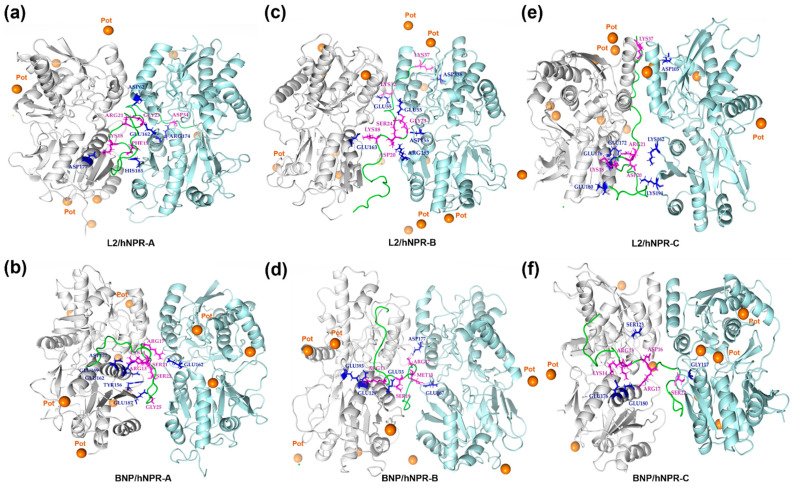
Figure 2.
PyMol representation of hydrogen interactions detected between natriuretic receptors (NPRs) and L2 (a,c,e) and BNP (b,d,f). NPR dimers, L2 and BNP are represented in cartoons. Below, A, B and C are the chains of the natriuretic receptors (A and B are the chains of NPR-A and NPR-C and A and C are the chains of NPR-B). (a) The amino acids of L2, Phe15, Lys18, Arg21, Gly23, and Asp34 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-A His185 (B), Asp177 (A), Asp62 (B), Glu162 (B) and Arg175 (B), respectively. (b) The amino acids of BNP, Arg13, Lys14, Arg17, Ser21, Ser22, and Gly25 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-A Tyr156 (A), Glu162 (A), Glu 169 (A), Asp77(A), and Glu162 (B), respectively. (c) The amino acids of L2, Lys18, Asp20, Gly23, Ser24, LYS32, and Lys37 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-B Glu163 (A), Arg183 (C), Asp155 (C), Glu55 (C), Glu55 (A), and Asp338 (C), respectively. (d) The amino acids of BNP, Arg13, Met15, Arg17, and Ser19 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-B Glu129 (A), Glu167 (A), Asp155 (C) and Glu55 (C), respectively. (e) The amino acids of L2, Lys18, Asp20, Arg21, and Lys37 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-C Glu176 (A), Lys194 (B), Glu176 (A), and Asp105 (B), respectively. (f) The amino acids of BNP, Arg13, Lys14, Asp16, Arg17, and Ser22 form hydrogen bonds with NPR-C Glu180 (A), Glu1176 (A), Arg99 (A), Glu176 (A), and Gly117 (B), respectively. Lebetin 2 (L2) and human B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) are represented in green. The potassium ion (K+) are in orange, NPR monomer 1 in cyan blue and monomer in gray. L2 and BNP residues in purple are involved in interaction with NPR residues (in blue).