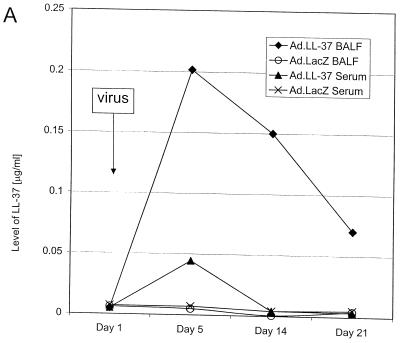
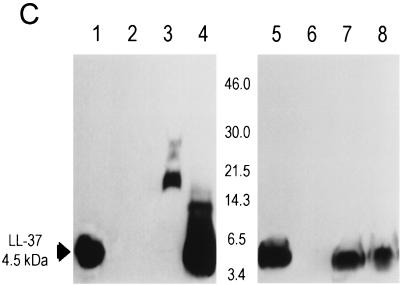
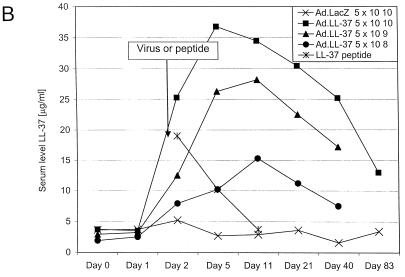
FIG. 1.
LL-37 in BALF and serum after administration of the recombinant virus or synthetic peptide. (A) Levels of LL-37 in BALF as determined by quantitative dot blot analysis. Virus was injected on day 1 of the experiment, and concentrations in BALF were determined on the following days. (B) Levels of LL-37 in serum as determined by quantitative dot blot analysis. Virus or peptide was injected on day 1 of the experiment, and concentrations in serum were determined by bleeding the animals and using the serum for qualitative dot blot analysis. (C) Western blots following denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions with Tricine gels of mouse serum and BALF, using a polyclonal antibody against LL-37/hCAP-18. Lanes: 1, 20 ng of synthetic LL-37 peptide; 2, serum from a mouse that received the control vector coding for β-galactosidase; 3, serum from a mouse that received the vector coding for LL-37/hCAP-18 (crude); 4, serum from a mouse that received the vector coding for LL-37/hCAP-18 (RP-HPLC purified); 5, 20 ng of synthetic LL-37 peptide; 6, BALF from a mouse that received the vector coding for β-galactosidase (crude); 7 and 8, BALF from a mouse that received the vector coding for LL-37/hCAP-18 (crude, lane 7; HPLC purified, lane 8).