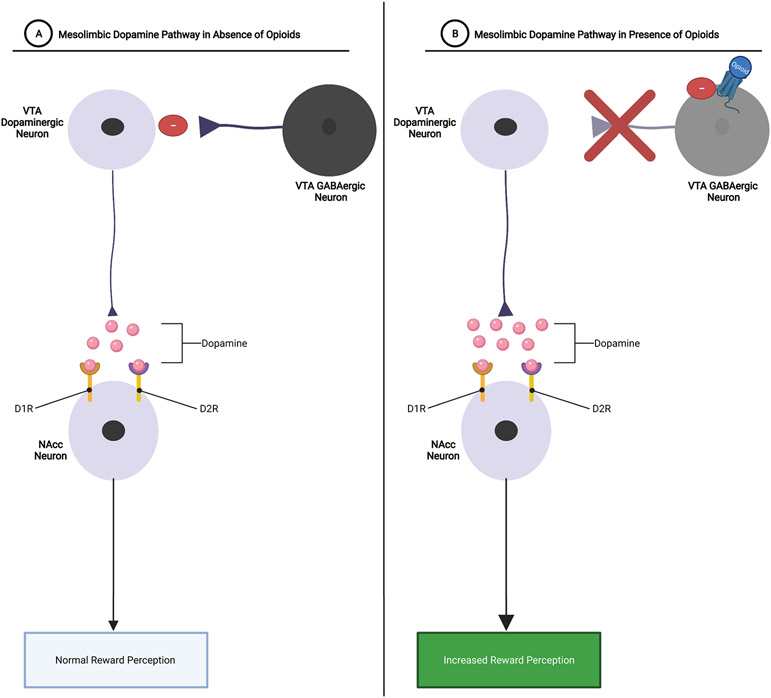
Figure 6: Mesolimbic Dopaminergic Signaling with and without Opioids:
A.) Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway in Absence of Opioids: VTA dopaminergic neurons release dopamine into the NAcc. Dopamine then binds to D1R and/or D2R dopamine receptors on NAcc neurons, resulting in reward perception. GABAergic neurons function as a reward “brake system” by inhibiting dopaminergic signaling within the mesolimbic pathway, thereby mediating how rewarding a particular stimulus is.
B.) Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway in Presence of Opioids: Opioids bind to Mu-receptors on VTA GABAergic neurons, thereby removing the reward brake system and allowing for larger amounts of dopamine to be released into the NAcc. Increased release of dopamine within the NAcc results in increased reward perception.