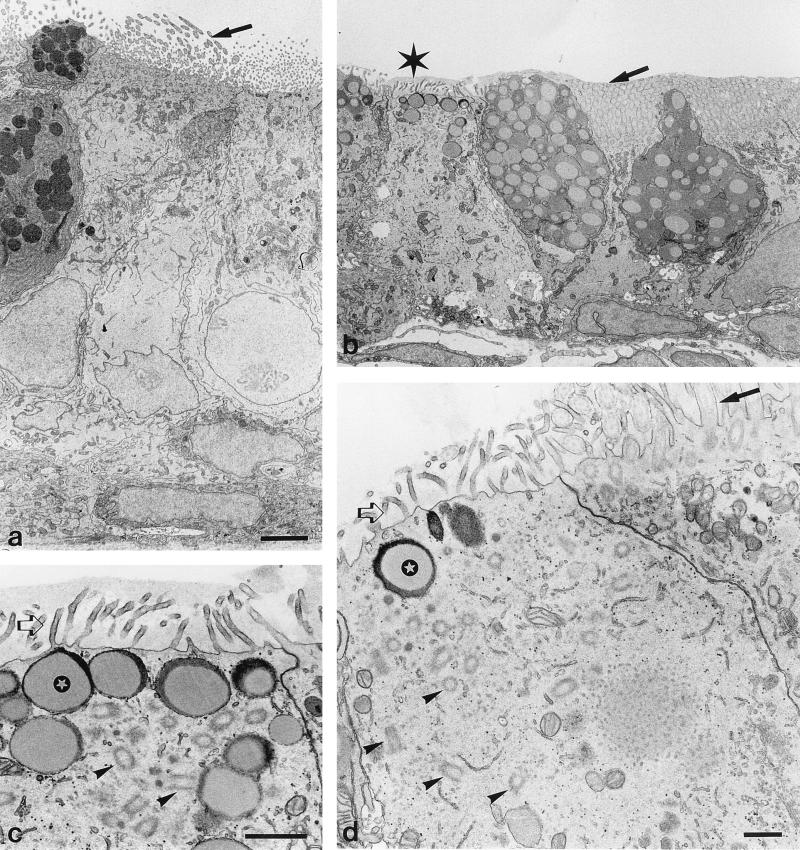
FIG. 2.
Transmission EM of ciliated epithelium of the eustachian tube. (a) Sham-treated specimen. (b to d) Effects of histamine treatment. Histamine was administered through the tympanic membrane 48 and 24 h before sacrifice. Histamine induces loss of cilia (indicated by the asterisk in panel b; this area is magnified in panel c). Mucous deposition is present after histamine treatment over and between cilia (b) and microvilli (c); in panel b, this mucous deposition results in clumping of cilia (arrow). These depositions are not observed after sham treatment (arrow in panel a). Microvilli (open arrows) are present with (c) and without (d) mucus on epithelial cells which have lost their cilia. These cells show numerous basal bodies in a disordered manner (arrowheads). Normal apical organization of cilia-associated basal bodies is shown in a cell in panel d, which also shows normal cilia (arrow); this apparent normal cell resides adjacent to a pathologic epithelial cell. Below the apical plasma membrane of pathologic cells there are vacuoles filled with a mucous substance (indicated by the stars in panels c and d). Bars, 3 μm (a and b), 1 μm (c), and 0.5 μm (d).