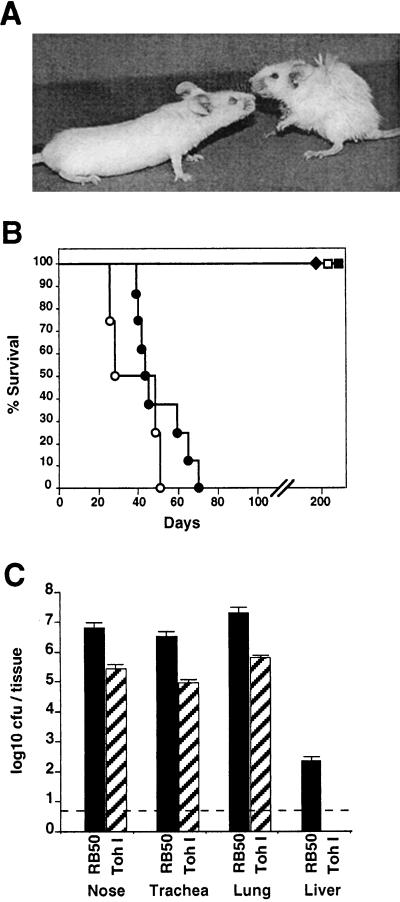
FIG. 4.
Comparison of B. bronchiseptica and B. pertussis infection of SCID-beige mice. (A) Representative mice were photographed on day 40 after intranasal inoculation with 50 μl of PBS containing 5 × 105 CFU of B. bronchiseptica (right) or B. pertussis (left). (B) Survival of SCID-beige mice inoculated with either B. bronchiseptica (circles) or B. pertussis (squares) is presented as a function of time. Bacteria were delivered intranasally at either a low-dose–low-volume of 500 CFU in a 5-μl PBS droplet (solid symbols) or a high-dose–high-volume of 5 × 105 CFU in 50 μl of PBS (open symbols). (C) Colonization of various tissues by B. bronchiseptica or B. pertussis. Groups of four 4-week-old female SCID-beige mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 CFU in 50 μl of PBS of either B. bronchiseptica (solid bars) or B. pertussis (hatched bars) and sacrificed at 45 days postinoculation, and the colonization levels in the nasal cavity, trachea, lungs, and liver were determined. The mean log10 CFU per organ or tissue is shown. The dashed line represents the lower limit of detection.