Figure 1.
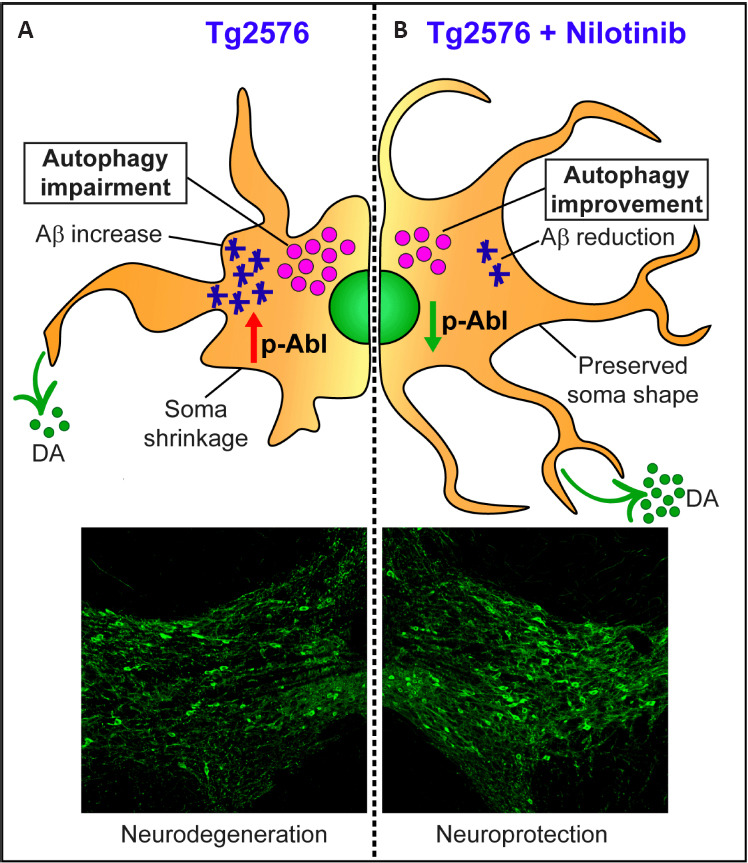
Nilotinib protects ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons from degeneration by the improvement of autophagic flux.
(A) VTA dopamine (DA) neurons from 3-month-old Tg2576 mice (disease onset) show increased phosphorylated levels of c-Abelson (c-Abl) and alteration in the autophagic flux that lead to accumulation of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ). During the disease progression, neurodegeneration is associated with cell shrinkage and is parallel with the reduction of DA levels in VTA-projecting areas, causing cognitive and non-cognitive deficits. (B) VTA DA neurons from Nilotinib-treated mice show the reduction of both c-Abl phosphorylated levels and autophagosome accumulation. The improvement of the autophagic flux promotes the reduction of Aβ and exerts neuroprotective effects, as demonstrated by the preserved soma shape and DA neuron number, shown in the representative confocal images (DA neurons are marked with tyrosine hydroxylase antibody). Nilotinib prevents the death of DA neurons of VTA, thus maintaining DA outflow in its target areas and ameliorating memory functions in Tg2576 mice. Unpublished data.
