Figure 7.
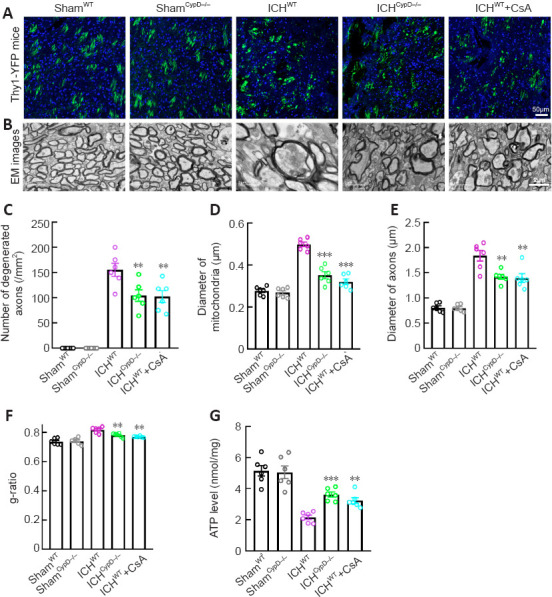
Effects of CypD deficiency and CsA treatment on axonal injury after ICH.
(A) Representative immunofluorescence micrographs of normal and degenerated axons in each group. (B) EM images of normal and degenerated axons and normal and swollen mitochondria morphology in each group. The mitochondrial and axonal diameters in the ICHCypD–/– and ICHWT + CsA groups were smaller than those in the ICHWT group. Scale bars: 50 μm in A, 2 μm in B. (C) Number of degenerated axons per mm2 around the hematoma in each group. The number of degenerated axons around the hematoma was significantly decreased in the ICHCypD–/– and ICHWT + CsA groups compared with that in the ICHWT group. (D) Quantification of the diameter of mitochondria in each group. (E, F) The axonal diameters (E) and mean g-ratio of the WM (F) around the hematoma in each group. (G) Quantification of ATP levels in tissue around the hematoma in each group. For data collection, three sections of each mouse and three visual fields around the hematoma of each section were observed. At least 50 degenerated axons and swollen mitochondria were measured for each mouse. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 6 animals for each group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. ICHWT group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). CsA: Cyclosporin A; CypD: cyclophilin D; EM: electron microscopy; ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage; WT: wild type.
