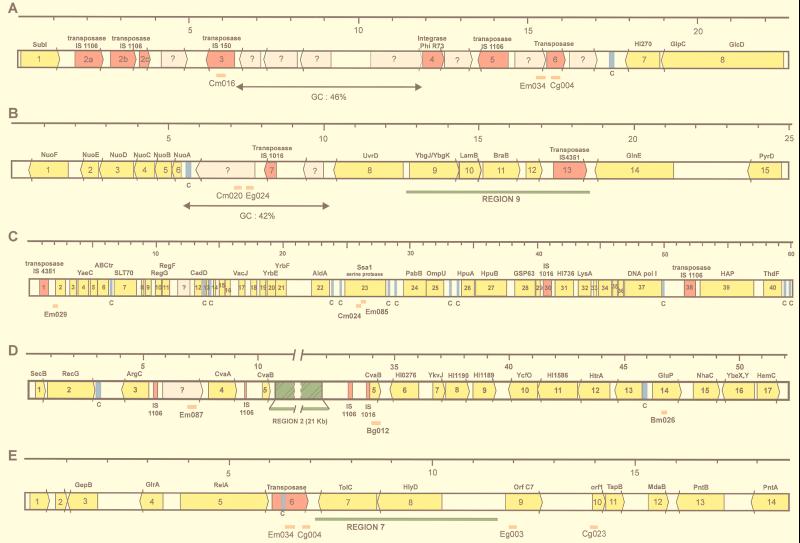
FIG. 4.
Genetic arrangement of the regions surrounding pathogen-specific clones. Genes are shown as arrows, yellow for those with homologies to proteins in the databases and grey for ORFs without significant homology. Transposases are shown in red, and Correia sequences (marked C) are shown in blue. The positions of the subtractive clones are shown as orange bars below the bar representing the genes. Regions previously discovered as being N. meningitidis specific are shown in green. A scale (in kilobases) is shown above the sequences. (A) The pathogen-specific clones flank a region of low G+C content (46%) containing several ORFs with no homologies to previously described genes. Homologies of surrounding ORFs, at the amino acid level, are as follows: 1, SubI, E. coli; 2a, 2b, 2c, transposase, IS1106, N. meningitidis; 3, ORF B, IS150, E. coli; 4, integrase, phage φR73; 5, transposase IS1106, N. meningitidis; 6, transposase, Synechocystis sp. (accession no. BAA10234); 7, (3′ end) HI0270, H. influenzae; 8, (5′ end) GlcD, Synechocystis sp. (3′ end) and GlpC, Helicobacter pylori. (B) The pathogen-specific clones correspond to a region of particularly low G+C content (42%), containing ORFs with no homologies. Homologies of surrounding ORFs, at the amino acid level, are as follows: 1, NuoF, Rickettsia prowazekii; 2, NuoE, R. prowazekii; 3, NuoD, R. prowazekii; 4, NuoC, Rhodobacter capsulatus; 5, NuoB, Rickettsia prowazekii; 6, NuoA, Sinorhizobium meliloti; 7, transposase, IS1016, H. influenzae; 8, UvrD, E. coli; 9, HI1731, H. influenzae; 10, LamB homolog, H. influenzae; 11, BraB homolog, H. influenzae; 12; MTH939, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum; 13, transposase IS4351, N. meningitidis; 14, GlnE, E. coli; 15: PyrD, Salmonella typhimurium. (C) Homologies are as follows: 1, transposase IS4351, N. meningitidis; 2, ORF 288, Coxiella burnetii; 3, ORF 1244, Sphingomonas aromaticivorans; 4, YaeC, E. coli; 5, YaeE, E. coli; 6, ABC transporter (accession no. P30750), E. coli; 7, SLT70 transglycosylase (accession no. S56616), E. coli; 8, ribosomal protein S21, Burkholderia pseudomallei; 9, LporfX, Legionella pneumophila; 10, RegG, N. gonorrhoeae; 11, RegF, N. gonorrhoeae; 12, CadD, Staphylococcus aureus; 13, ribosomal protein L31, Haemophilus ducreyi; 14, putative acetyltransferase (accession no. CAA90593), Schizosaccharomyces pombe; 15, ResA, Bacillus subtilis; 16, YbaW, E. coli; 17, VacJ, Rickettsia prowazekii; 18, YrbC, E. coli; 19, HI1085, H. influenzae; 20, HI1086, H. influenzae; 21, HI1087, H. influenzae; 22, AldA, E. coli; 23, SsaI, Pasteurella haemolytica; 24, PabB, Helicobacter pylori; 25, OmpU, N. meningitidis; 26, HpuA, N. gonorrhoeae; 27, HpuB, N. meningitidis; 28, GroEL, N. gonorrhoeae; 29, GroES, N. gonorrhoeae; 30, transposase, IS1016, H. influenzae; 31, HI0736, H. influenzae; 32, LysA, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; 33, CyaY, E. coli; 34, HI1643, H. influenzae; 35, HI0931, H. influenzae; 36, YgaG, E. coli; 37, PolA, H. influenzae; 38, transposase IS1106, N. meningitidis; 39, Hap, H. influenzae; 40, ThdF, E. coli. (D) The subtractive clones flank the previously discovered N. meningitidis-specific region 2. Homologies are as follows: 1, SecB, E. coli; 2, RecG H. influenzae; 3, ArgC, Synechocystis sp.; 4, CvaA, plasmid ColV, E. coli; 5, CvaB, plasmid ColV, E. coli; 6, HI0276, H. influenzae; 7, YkvJ, Bacillus subtilis; 8, HI1190, H. influenzae; 9, HI1189, H. influenzae; 10, YcfO, 11, HI1586, H. influenzae; 12, MucD/HtrA serine protease homolog, Pseudomonas; 13, (5′ end) HI0489, H. influenzae, (3′ end) Nth endonuclease III, H. influenzae; 14, GluP, Brucella abortus; 15, NhaC, Bacillus firmus; 16, (5′ end) YbeY, E. coli, (3′ end) YbeX, E. coli; 17, HemC, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (E) Homologies are as follows: 1, aq_1853, hypothetical protein, Aquifex aeolicus; 2, C09_orf404, Mycoplasma pneumoniae; 3, GepB, Dichelobacter nodosus; 4, GlrA, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans; 5, RelA, Vibrio sp.; 6, putative transposase (accession no. AAD10186), Streptococcus pneumoniae; 7, TolC, E. coli; 8, HlyD, E. coli; 9, ORF C7, Ralstonia solanacearum/RstA1, CTX phage, Vibrio cholerae; 10, ORF1, TspB, N. meningitidis; 11, TspB, N. meningitidis; 12, MdaB, H. influenzae; 13, PntB, H. influenzae; 14, PntA, E. coli.