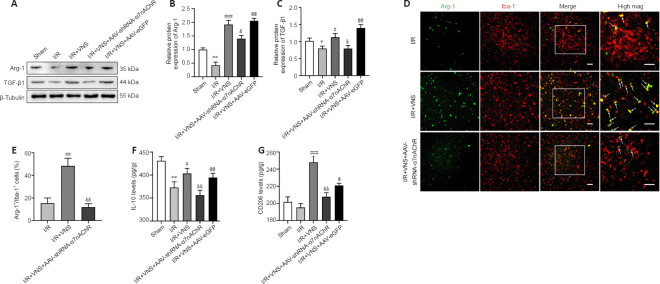
Figure 3.
VNS promotes the microglial regulatory phenotype through α7nAchR after cerebral I/R injury.
(A–C) Protein level of the microglial regulatory phenotype markers Arg-1 and TGF-β1 at day 3 after MCAO. (D) Immunofluorescence images showed Arg-1 expression in the peri-infarction cortex. Arg-1 (Alexa Fluor 488 labeled green) localized to the microglia marker Iba-1 (Alexa Fluor cy3 labeling red) with areas of overlap appearing yellow in the merged image (white arrow). Increased Arg-1(+) and Iba-1(+) microglia were noted in the I/R + VNS group compared with that in the I/R group, and the increase in the number of these cells in the I/R + VNS group was reversed in the I/R + VNS + AAV-shRNA-α7nAchR group. Scale bars: 50 μm. (E) The percentage of Arg-1+/Iba-1+ cells. (F, G) Effect of I/R, VNS + I/R, and I/R + VNS + AAV-shRNA-α7nAchR treatments on IL-10 (F) and CD206 (G) levels in the peri-infarction cortex at 3 days after MCAO. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, vs. I/R group; &P < 0.05, &&P < 0.01, vs. I/R + VNS group; @P < 0.05, @@P < 0.01, vs. I/R + VNS + AAV-shRNA-α7nAchR group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). α7nAchR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; AAV: targeting adeno-associated virus; Arg-1: Arginase-1; IL-10: interleukin-10; I/R: ischemia/reperfusion; mag.: image; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; shRNA: short hairpin RNA; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor beta1; VNS: vagus nerve stimulation.