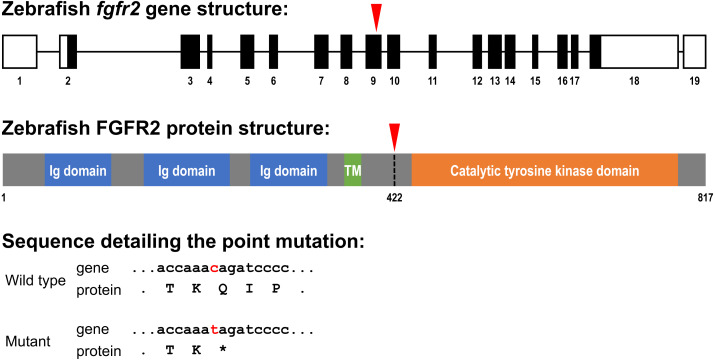
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the zebrafish fgfr2 gene and protein structure.
(A) Five highly similar transcript variants have been found; variant 1 is depicted here (transcript fgfr2-201 in Ensembl; NCBI Reference Sequence: NM_001243004.1). The fgfr2 gene consists of 19 exons, of which 17 coding exons. Note that the exons (depicted as boxes) are drawn on a 20-times larger scale than the introns (depicted as lines). The full gene transcript is 4,741 bp long; the coding sequence is 2,451 bp running from exon 2 to exon 18 (indicated by black filling). The red arrowhead pointing down indicates the site of the mutation in the fgfr2 sa10729 mutant zebrafish used in the current study. (B) The gene encodes an 817 amino acid protein. The protein is characterized by three immunoglobulin (Ig) domains, a transmembrane (TM) region and a tyrosine kinase domain. The truncated FGFR2 protein that results from the mutation consists of 421 amino acids (premature stop codon indicated by the red arrowhead pointing down). (C) Partial nucleotide (lower case) and amino acid (upper case) sequence detailing the point mutation. The c > t mutation causes a stop codon (indicated by the asterisk).