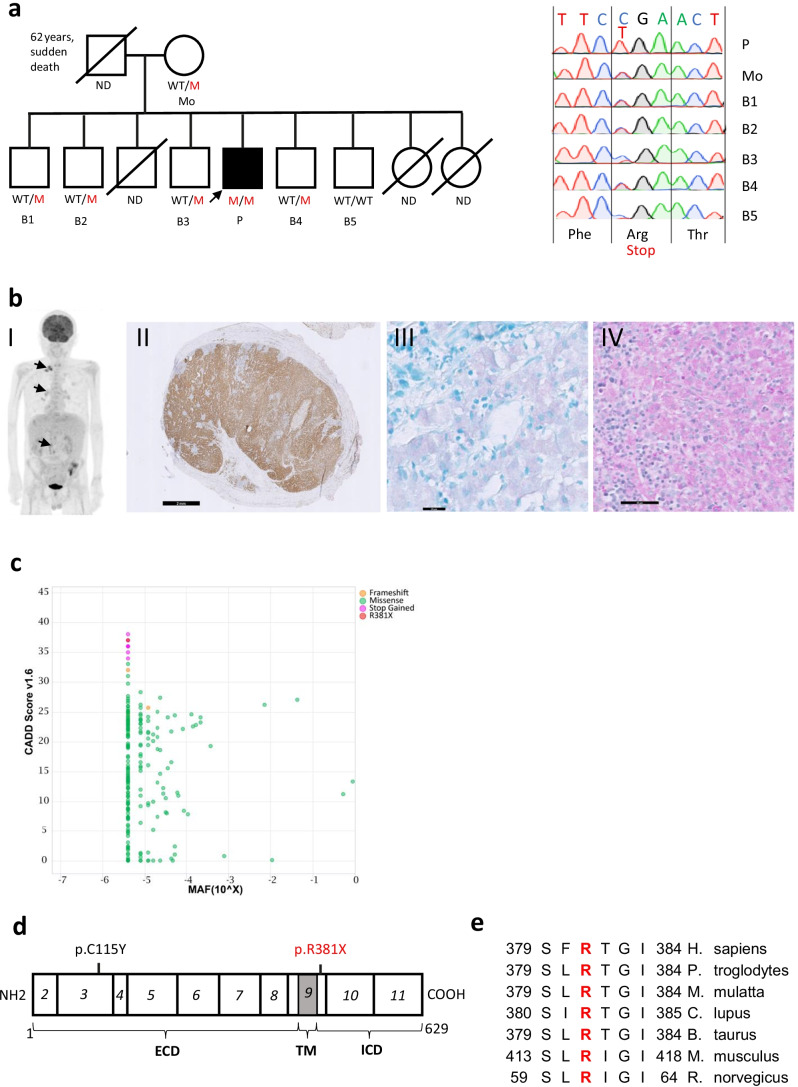
Fig. 1.
Identification of a homozygous c.1141C > T (p.R381X) in a patient with MSMD. a Family pedigree with genotype. ND = not determined. M = mutant. WT = wild type. Sanger chromatogram shown for all tested individuals. b b.I clinical presentation with multifocal adenopathies on PET CT scan resulting from disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial disease, b.II CD68 staining showing diffuse histiocytic infiltration in a lymph node, b.III Positive Ziehl–Neelsen staining in macrophages on a duodenal biopsy, b.IV Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining on bone marrow highlighting numerous PAS-positive micro-organismas within macrophage. Scale bars are depicted in black (2 mm, 20 µm and 50 µm). c Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD) score and allelic frequency (MAF) of the c.1141C > T (p.R381X) mutation and other predicted LOF heterozygous mutations in gnomAD. d Schematic linear protein structure of IL23R (629 aa) and exons (italic) encoding the extracellular domain (ECD), transmembranous domain (TM) and intracellular domain (ICD). The studied mutation (p.R381X) is indicated in red, a previously identified pathogenic mutation (p.C115Y) in black. e conservation of the R381 residue among mammalian species