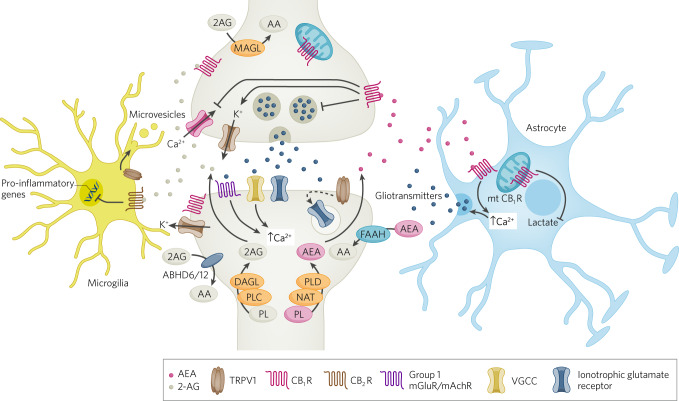
Fig. 1. Cellular aspects of eCB signaling.
Schematic diagram of eCB signaling elements within synapses, astrocytes and microglia. At the synapse, eCBs are synthesized postsynaptically, through a variety of mechanisms that result in increases in intracellular calcium, and activate presynaptic CB1 receptors to mediate retrograde suppression of neurotransmitter release. AEA can also activate TRPV1 receptors to initiate postsynaptic LTD via glutamate receptor internalization. CB1 receptors expressed on astrocytes can lead to increases in calcium release and release of gliotransmitters, which can indirectly affect synaptic transmission. CB2 receptors on microglia can regulate cytokine release. CB1 receptors expressed on mitochondria can also regulate a variety of intracellular processes including cellular energetics.