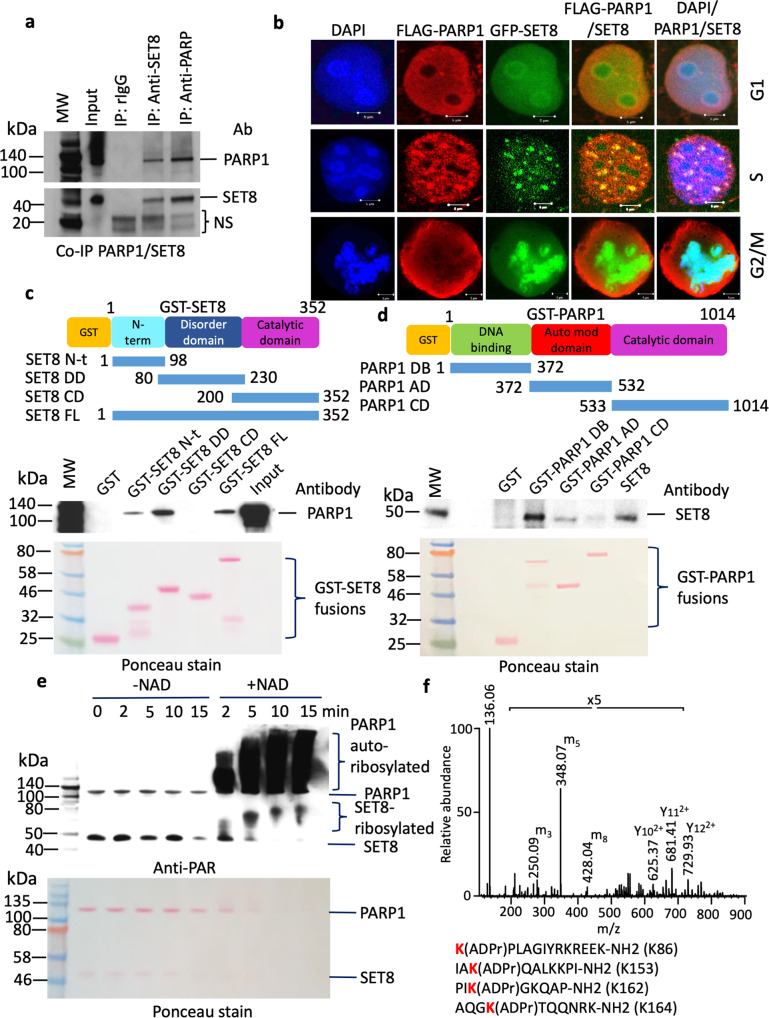
Fig. 1. Colocalization, binding, and poly ADP-ribosylation of SET8 by PARP1.
a Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous SET8 and PARP1 in HCT116 cells. Rabbit IgG (left lane) was used as a negative control. Non-specific bands are represented as NS. b Colocalization between FLAG-PARP1 (red) and GFP-SET8 (green) during cell cycle in COS-7 cells. DAPI (blue) represents the nuclear DNA content. c, d Mapping of domain interactions using GST-pulldown assays between SET8 domains (top, left) and full-length recombinant PARP1 protein and GST-pulldown assays between PARP1 domains and full-length recombinant SET8 protein (top, right). The PARP1 or SET8 binding were detected by western blotting using PARP1 antibody (middle, left) or SET8 antibody (middle, right), respectively. Ponceau stain gels (bottom) represent the amount of GST beads constructs used for the GST-pulldown assays. e In vitro detection of full-length recombinant SET8 ADP-ribosylation by full-length recombinant PARP1 by western blotting using anti-ADP ribose antibody (top). Ponceau stain gels (bottom) represent the amount of PARP1 and SET8 recombinant enzyme used for ADP-ribosylation assay (bottom). f Detection of SET8 lysines ADP-ribosylation using mass spectrometry analysis of SET8 ADP-ribosylated peptides by full-length recombinant PARP1 protein in vitro.