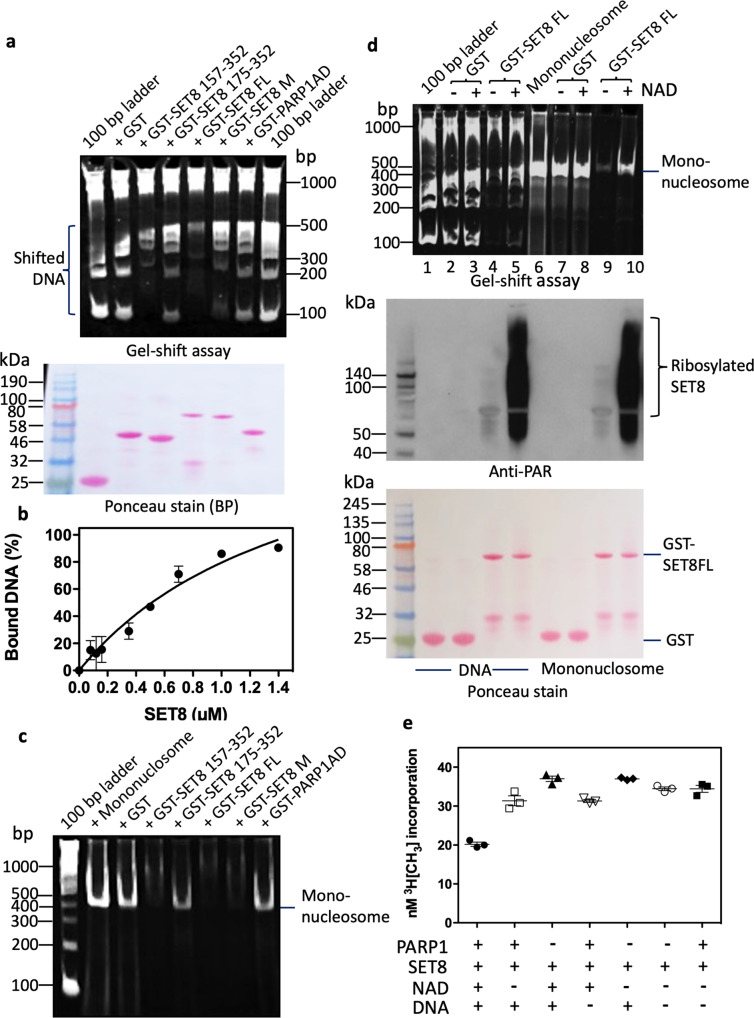
Fig. 2. Poly ADP-ribosylation impairs DNA, nucleosome binding, and catalytic activity of SET8 protein.
a Detection of unbound 100 bp DNA ladder by TBE ethidium bromide-stained gel in supernatants (left lane) on GST-SET8 domains or mutant (M) using GST-pulldown assays (top, left side). Asterisks are representing shift of DNA on GST-SET8 157–352 amino acid protein or GST-SET8 full-length protein (FL) beads. Ponceau stain represents the amount of GST beads constructs used for the GST-pulldown (bottom, left side). b Different concentrations of recombinant full-length SET8 protein binding to DNA using EMSA to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd). c Detection of unbound mononucleosome by TBE ethidium bromide-stained gel in supernatants on GST beads versus GST-SET8 domains or mutant (M) beads using GST-pulldown assays. d Detection of unbound DNA (left side) or unbound mononucleosome (right side) by TBE ethidium bromide-stained gel in supernatants (top) on GST beads versus GST-SET8 FL beads using GST-pulldown assays. GST or GST-SET8 FL beads were poly ADP-ribosylated or not (with or without NAD) using full-length recombinant PARP1 as demonstrated by western blot using anti-ADP ribose antibody (middle). Ponceau stain gel (bottom) represents the amount of GST bead constructs used for the GST-pulldown and the ADP-ribosylation western blot analysis. e SET8 histone methyltransferase assay on full-length recombinant histone H4 using full-length recombinant SET8 in the presence or absence of activated full-length recombinant PARP1.