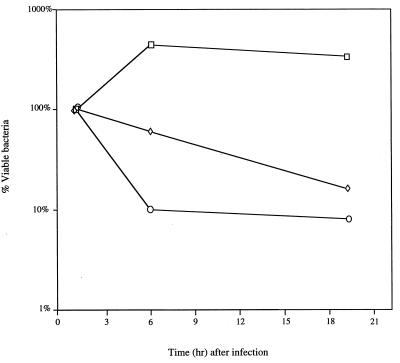
FIG. 2.
Survival of S. typhimurium derivatives in murine peritoneal macrophages. Macrophages were harvested from the peritoneal cavity of 6- to 8-week-old BALB/c mice 3 days after intraperitoneal injection with 1.5 ml of 10% sterilized proteose peptone (Difco). Macrophages removed from the peritoneal cavity with a 23-gauge needle and 30-ml syringe were resuspended in endotoxin-free RPMI medium containing 5% fetal calf serum and 1 U of heparin per ml. Contaminating erythrocytes were removed by centrifugation, and the number of viable macrophages was quantitated on a hemocytometer following the addition of trypan blue. Approximately 105 peritoneal macrophages were seeded per well in 48-well tissue culture plates. Macrophages were allowed to adhere for 1 h in a 37°C incubator containing 5% CO2. Bacteria were diluted in 0.85% NaCl, centrifuged, and resuspended in 25% mouse serum. After opsonization in mouse serum at 37°C for 15 min, RPMI medium was added to give a final multiplicity of infection of bacteria to macrophages of between 1 and 5. Immediately after the addition of bacteria, tissue culture plates were centrifuged to promote bacterial adherence. Bacterial internalization was allowed to proceed for approximately 30 min, and then each reaction mixture was divided into two aliquots. In one aliquot, extracellular bacteria were killed by the addition of RPMI buffer containing 12.5 μg of gentamicin per ml. Macrophages were lysed with 0.5% deoxycholate, and the number of bacteria in each aliquot was determined by spotting serial dilutions onto rich medium plates. The number of internalized bacteria was initially determined 1.5 h after gentamicin treatment. Survival in macrophages was determined after 6 and 19 h of incubation. The number of surviving bacteria at these times is expressed as a percentage of the number of bacteria internalized. Values represent the mean from experiments performed in triplicate. The standard error was <2.0% of the mean for all values. Strains were wild-type (□), mutS recD (◊), or recA (○) derivatives of S. typhimurium 14028s.