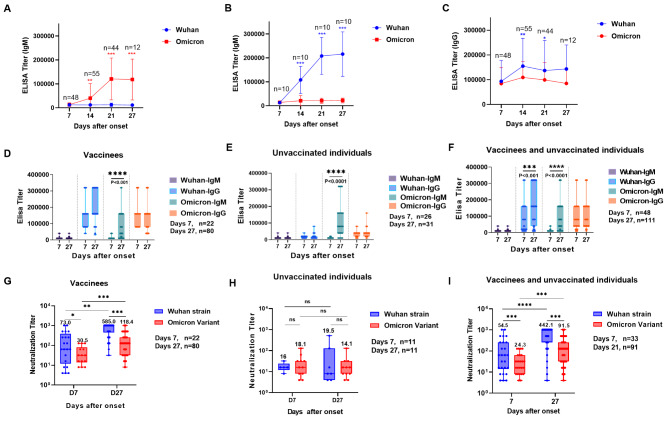
Fig. 1.
Assessment of antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in unvaccinated individuals and vaccinees from Omicron-BA.2 infection
(A-B) Kinetics of anti-RBD IgM antibody titers of sera from Omicron-infected individuals (A) and Wuhan strain-infected individuals (B) against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain and Omicron-BA.2 strain during 7–27 days after onset using the ELISA assay. (C) Kinetics of anti-RBD IgG antibody titers of sera from Omicron-infected individuals against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain and Omicron-BA.2 strain during 7–27 days after onset using the ELISA assay.The titers were calculated at 450nm (OD50), and serum samples from 7 days, 8 to 14 days, 15 to 21 days, and 22 to 27 days after onset were tested respectively. (D-F) Dynamic change of anti-RBD IgM and IgG antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain and Omicron-BA.2 strain in vaccinees of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine (panel D) or unvaccinated individuals (panel E) or all COVID − 19 patients (panel F) in the 0–7 days or 8–27 days after onset. (G-I) Dynamic change of neutralization antibody titers against authentic SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain and Omicron-BA.2 variant in vaccinees of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine (panel G) or unvaccinated individuals (panel H) or all COVID − 19 patients (panel I) in the 0–7 days or 8–27 days after onset. Geometric mean titers (GMT) of neutralizing antibodies were shown. The sample size for each panel was shown as n. P values were obtained from a comparison between the two treatment groups using t-tests for long-transformed antibodies or two-sided χ2 tests for categorical data. Multiple comparisons of antibody titers were performed using the Welch’ t-test