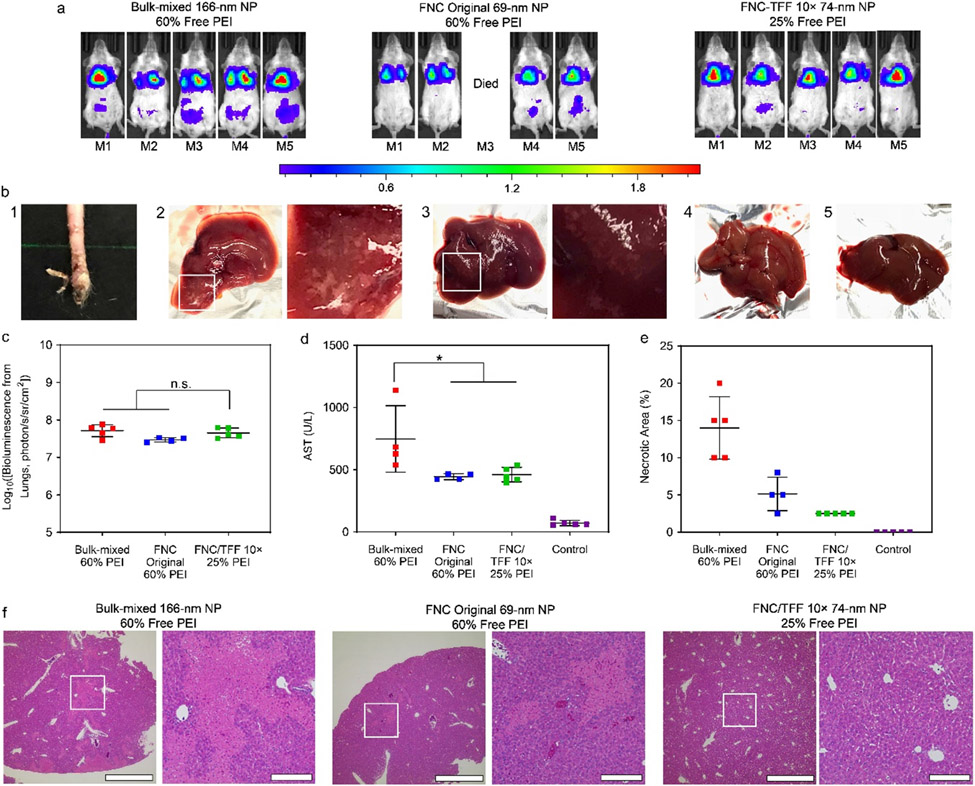
Figure 3.
(a) In vivo transfection efficiency of the injected Polyplus bulk-mixed, FNC original and FNC/TFF 10× pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles, respectively in Balb/c mice. The injection dose is 40 μg DNA/mice. IVIS whole-body images were taken at 24 h post injection of particles. Scale bar: local radiance with unit of 106 photon/s/sr/cm2 (b) 1: The necrosis at the tail injection site of the unpurified nanoparticles. The images of harvested livers in each group. 2: Polyplus bulk-mixed, 3: FNC original, 4: FNC/TFF 10× pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles, 5: Naked DNA. (c) The IVIS ROI quantitative analysis results at 24 h time point from Balb/c mice. Each bar represents mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). (d) AST assessments of Balb/c mice injected with Polyplus bulk-mixed, FNC original, and FNC/TFF 10× pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles, respectively. (e) Percentage of necrotic area in liver of Balb/c mice injected with Polyplus bulk-mixed, FNC original, and FNC/TFF 10× pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles, respectively. (f) H&E-stained liver tissue sections of Balb/c mice injected with Polyplus bulk-mixed, FNC original, and FNC/TFF 10× pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles, respectively. Scale bar 1000 μm (Left) and 200 μm (Right). For statistical analysis, n.s. denotes no statistical significance with p > 0.05 and *p < 0.05 from one-way ANOVA test.