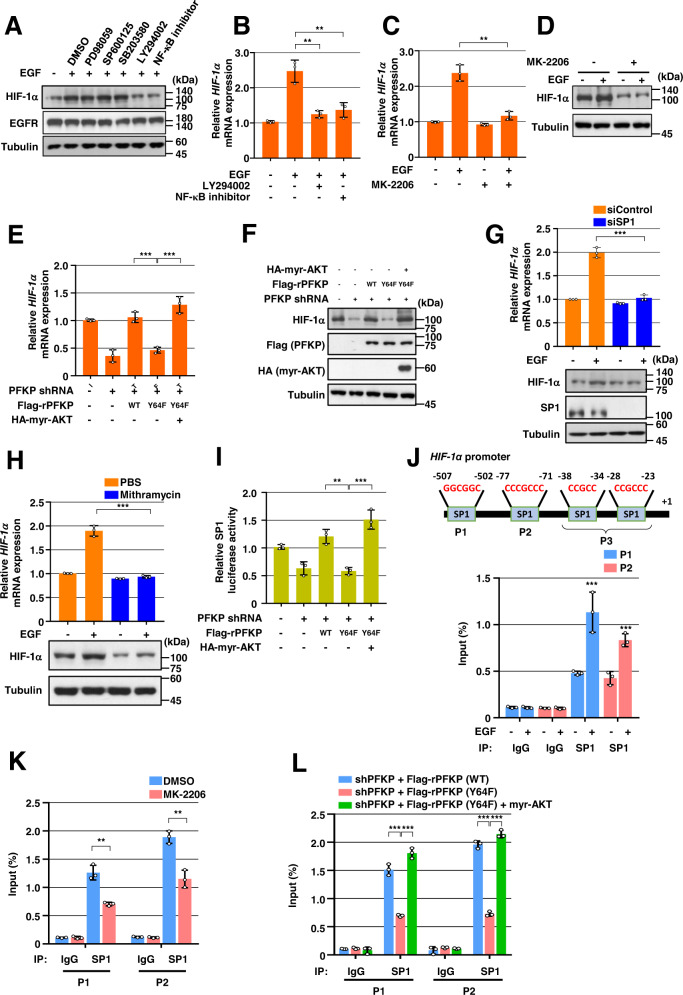
Fig. 2. PFKP Y64 phosphorylation induces EGFR activation-enhanced HIF-1α transcriptional expression through SP1 transactivation.
WB and qRT-PCR were performed with indicated primers and antibodies, respectively (A–H). A Serum-starved GSCs were pretreated DMSO, PD98059 (20 μM), SP600125 (25 μM), SB203580 (10 μM), LY294002 (20 μM), or NF-κB inhibitor (1 μM) for 1 h and then stimulated with or without EGF (100 ng/mL) for 12 h. B–D Serum-starved GSCs were pretreated DMSO, LY294002, NF-κB inhibitor (B), or MK-2206 (5 μM) (C, D) for 1 h and then stimulated with or without EGF (100 ng/mL) for 12 h. E, F LN229/EGFRvIII cells with or without PFKP depletion and with or without reconstituted expression of WT Flag-rPFKP or Flag-rPFKP Y64F mutant in the presence or absence of HA-myr-AKT expression. G GSCs were transfected with control siRNA or SP1 siRNA. H GSCs were treated with PBS or mithramycin (500 nM) for 12 h. I SP1 luciferase activity in LN229/EGFRvIII cells with or without PFKP depletion and with or without reconstituted expression of WT Flag-rPFKP or Flag-PFKP Y64F mutant in the presence or absence of HA-myr-AKT expression was measured. J–L ChIP assays were performed with anti-SP1 antibody, and real-time PCR analyses were performed with primers against the HIF-1α promoter. (J) A schematic of the putative SP1 binding site (Marked as P1–P3) on the HIF-1α promoter region (J; upper panel). GSCs were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/mL) for 12 h (J; bottom panel). K LN229/EGFRvIII cells were pretreated with DMOS or MK-2206 (5 μM) for 1 h and then treated with EGF (100 ng/ml) for 12 h. L LN229/EGFRvIII cells with PFKP depletion and with or without reconstituted expression of WT Flag-rPFKP or Flag-rPFKP Y64F mutant were transfected with or without HA-myr-AKT. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments (B, C, E, G, H–L). ***P < 0.001, based on the Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.