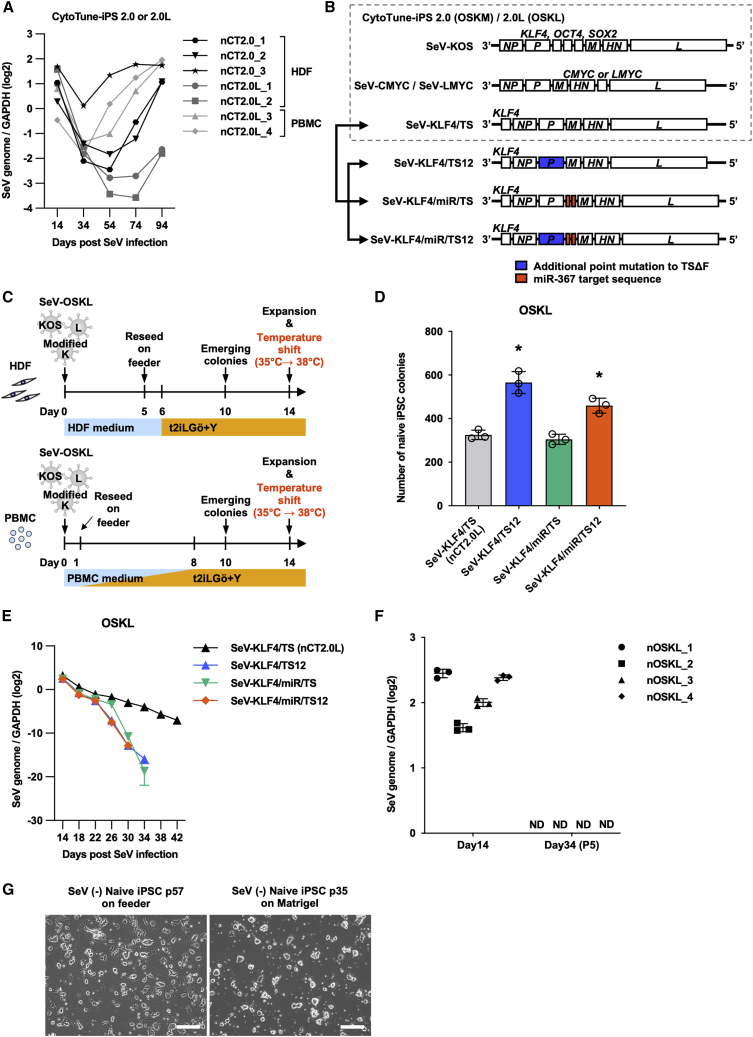
Figure 1.
Reprogramming HDFs and PBMCs into naive human iPSCs with a fast SeV vector removal system and modified SeV-KLF4 vectors
(A) qPCR analysis of SeV genome expression in naive iPSCs reprogrammed with the CytoTune 2.0 or 2.0L SeV reprogramming kit using TaqMan probes. Values are normalized to GAPDH expression and shown as the mean ± SD. n = 3 for each point.
(B) Schematic structure of the SeV vectors and the modified reprogramming cocktail. We changed the SeV18 + KLF4/TSΔF (KLF4/TS) vector in the CytoTune-2.0 or 2.0L reprogramming kit to one of three modified vectors: SeV18 + KLF4/TS12ΔF (KLF4/TS12), SeV18 + KLF4/PmiR367T2/TSΔF (KLF4/miR/TS), or SeV18 + KLF4/PmiR367T2/TS12ΔF (KLF4/miR/TS12). KLF4/miR/TS12 was developed for this study.
(C) Experimental design for the derivation of naive human iPSCs from HDFs or PBMCs using the modified SeV-OSKL cocktail and incubation temperature shift after the generation of naive human iPSCs.
(D) Number of naive human iPSC colonies generated from HDFs at day 14. Each of the SeV-KLF4/TS vectors was co-infected with SeV-KOS and SeV-LMYC. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. n = 3. ∗p < 0.05.
(E) qPCR analysis of SeV genome expression in naive iPSCs derived from HDFs reprogrammed with SeV-KOS, SeV-LMYC, and the respective SeV-KLF4 vectors using TaqMan probes. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. n = 3 of each point.
(F) qPCR analysis of SeV genome expression in HDF-derived naive iPSCs (nOSKL_1, 2) and PBMC-derived naive iPSCs (nOSKL_3, 4) reprogrammed with SeV-KOS, SeV-LMYC, and SeV-KLF4/miR/TS12 vectors at days 14 and 34 using TaqMan probes. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. n = 3.
(G) Representative phase-contrast images of naive iPSCs reprogrammed with SeV-KOS, SeV-LMYC, and SeV-KLF4/miR/TS12 vectors on iMEF feeder cells or in feeder-free conditions. Scale bars, 200 μm.